Beryllium (Be) Orbital diagram, Electron configuration, and Valence electrons
Beryllium has an atomic number of 4 belongs to Group 2 also known as the alkaline metal group. It is situated in the s-block of the periodic table. Beryllium has the symbol Be and “It is a relatively rare element in the universe”.
In this article, we will discuss – The beryllium Orbital diagram, Electron configuration, and Valence electrons in detail.
Orbital diagram:- A orbital diagram is simply a pictorial representation of the arrangement of electrons in the orbital of an atom, it shows the electrons in the form of arrows, also, indicates the spin of electrons.
Electron configuration:- Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in atomic orbitals. It shows the electrons in numbers, It doesn’t show the details on the spin of electrons like the orbital diagram.
Valence electrons:- Valence electrons are the simply outermost electron of an atom situated in an outermost shell surrounding an atomic nucleus. They can participate in the formation of chemical bonds.
How to find Electron configuration of Beryllium (Be)?
The electron configuration of Beryllium can be found using the Aufbau principle.
Aufbau Principle:
- The word ‘Aufbau’ in German means ‘building up’.
- The Aufbau rule simply gives the order of electrons filling in the orbital of an atom in its ground state.
- It states that the orbital with the lowest energy level will be filled first before those with high energy levels. In short, the electrons will be filled in the orbital in order of their increasing energies.
- For example, the 1s orbital will be filled first with electrons before the 2s orbital.
Simply understand that there are commonly four different types of subshells – s, p, d, and, f.
These subshells can hold a maximum number of electrons on the basis of a formula, 2(2l + 1) where ‘l’ is the azimuthal quantum number.
Value of ‘l’ for different subshells.
| Subshells | Value of ‘l’ | Maximum number of electrons, 2(2l + 1) | Number of orbitals in the subshell |
| s | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| p | 1 | 6 | 3 |
| d | 2 | 10 | 5 |
| f | 3 | 14 | 7 |
So, in short, the s subshell can hold a maximum of 2 electrons(1 orbital), the p subshell can hold 6 electrons(3 orbitals), the d subshell can hold 10 electrons(5 orbitals), and the f subshell can hold at most 14 electrons(7 orbitals).
Now, the electron configuration of an atom can be built by filling the electrons in a lower energy subshell first then higher, higher, and higher.
Generally, (n + l) rule is used to predict the energy level of subshells.
n = principle quantum number
l = Azimuthal quantum number
⇒ Lower the value of (n + l) for an subshell, the lower its energy, hence, it will be filled first with electrons.
⇒ For two different subshells having same (n + l) value, then the subshell with lower value of n has lower energy.
So, all these are basics of How filling of electrons will be done in different subshells, obviously, you don’t have so much time for writing electron configuration by using so many rules.
Therefore, we have a diagonal rule for electron filling order in the different subshells using the Aufbau principle.
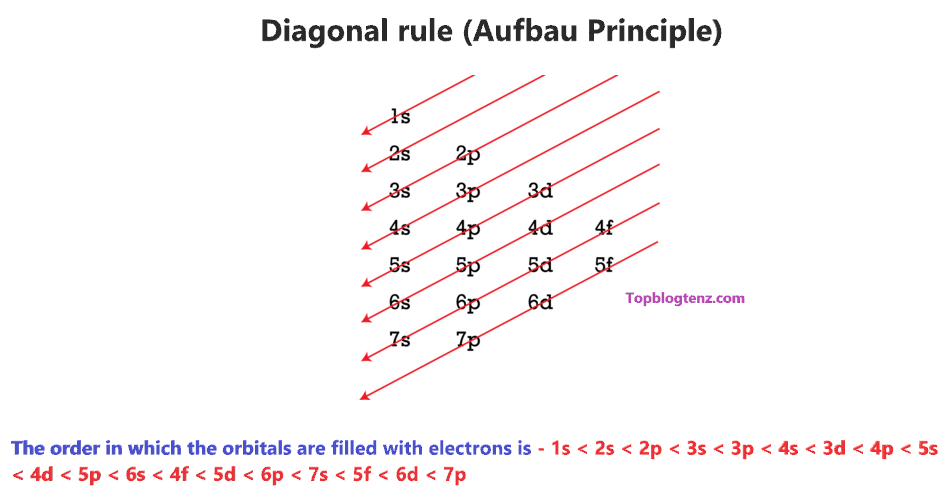
So, the order in which the orbitals are filled with electrons from lower energy to higher energy is – 1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p < 4s < 3d < 4p < 5s < 4d < 5p < 6s < 4f < 5d < 6p < 7s < 5f < 6d < 7p and so on.
Beryllium Electron configuration using the Aufbau Principle
- A Beryllium atom is a neutral atom that has 4 atomic numbers which implies it has a total of 4 electrons.
- As per the Aufbau rule, the electrons will be filled into 1s orbital first then 2s, …so on.
- Now, for the electron configuration of Beryllium, the first 2 electrons will go in 1s orbital since s subshell can hold a maximum of 2 electrons.
- The remaining two electrons will go in the 2s orbital.
- Therefore, the electron configuration of Beryllium will be 1s22s2.
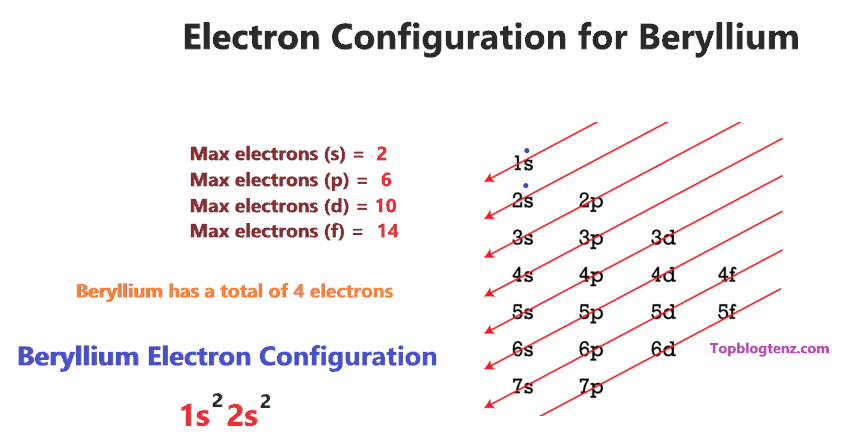
Beryllium (Be) Electron Configuration
Check – Electron configuration calculator to count the electron configuration for any atom
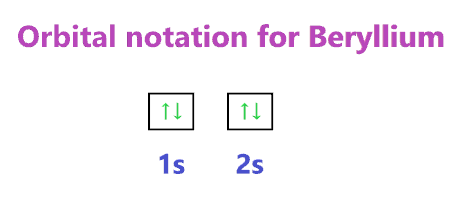
Orbital diagram for Beryllium
The orbital diagram simply represents the arrangement of electrons in the different orbitals of an atom, it uses an arrow to represent the electrons, every orbital(one box) contains a maximum of 2 electrons.
There are three rules followed for constructing the orbital diagram for an atom.
(1). Aufbau’s principle:- This rule state that the lower energy orbital will be filled before the higher energy orbital, for example – the 1s orbital will fill before the 2s orbital.
(2). Hund’s rule:- This rule state that each orbital of a given subshell should be filled with one electron each before pairing them. That means “Each orbital gets one electron first, before adding the second electron to the orbital”.
(3). Pauli Exclusion Principle:- This rule state that, no two electrons can occupy the same orbital with the same spin. That means “One must be spin up (↑) and one must be spin down (↓)”.
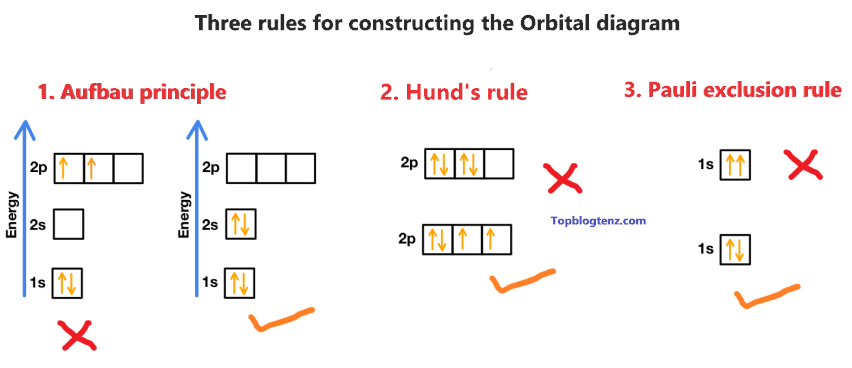
If you understand the above rules then constructing the orbital diagram or orbital notation for Beryllium is super easy.
Basics of Orbital diagram:-
There are different types of orbitals – s, p, d, and, f. These orbitals contain a number of boxes that can hold a number of electrons. Let’s see.
Each box will hold a maximum of 2 electrons with opposite spin.
- S orbital contains 1 box that can hold a maximum of 2 electrons.
- P orbital contains 3 boxes that can hold a maximum of 6 electrons.
- D orbital contains 5 boxes that can hold a maximum of 10 electrons.
- F orbital contains 7 boxes that can hold a maximum of 14 electrons.
The orbital diagram will also be filled with the same order as described by the Aufbau principle. (1s < 2s < 2p < 3s……and so on.)
Also check –
What is the Orbital diagram for Beryllium?
We know the electron configuration of Beryllium is 1s22s2, now for drawing its orbital diagram, we need to show its electrons in form of an arrow in different boxes using Hund’s and Pauli exclusion rule.
- The orbital diagram of Beryllium contains 1s orbital, and 2s orbital. 1s orbital contains 1 box, 2s orbital also contains 1 box.
- Beryllium has a total of 4 electrons and one box can hold up to the two electrons.
- Therefore, the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital, and the next two will go in the 2s orbital.
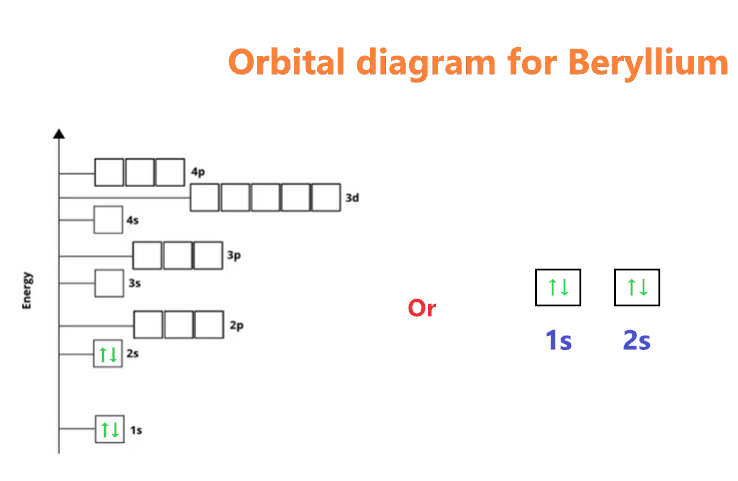
Beryllium Orbital diagram
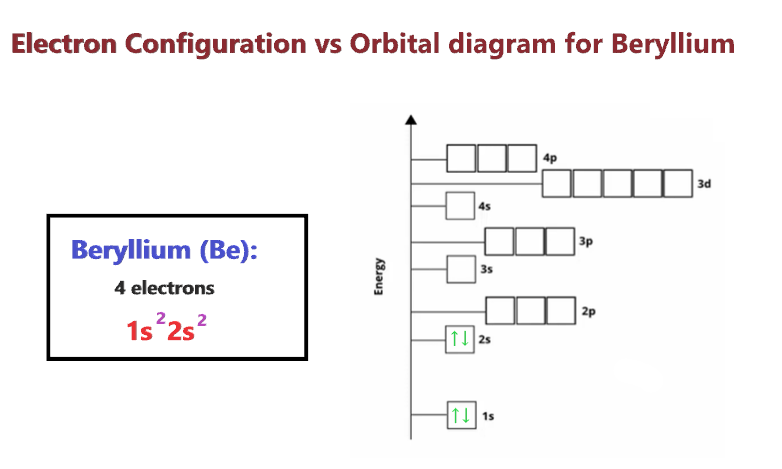
Electron configuration Vs Orbital diagram for Beryllium
The main difference between the orbital diagram and electron configuration is an orbital diagram shows electrons in form of arrows whereas an electron configuration shows electrons in form of numbers. Also, the orbital diagram shows details on the spin of electrons whereas the electron configuration doesn’t show it.
Both these follow the Aufbau principle (Diagonal rule).
Also Read:–
Electron configuration for Beryllium via Bohr model (Orbit)
Bohr model describes the visual representation of orbiting electrons around the small nucleus. It used different electron shells such as K, L, M, N…so on.
These electron shells hold a specific number of electrons that can be calculated via the 2n2 formula where n represents the shell number.
| Electron shells | Shell number (n) | Max. number of electrons (2n2) |
| K | 1 | 2 |
| L | 2 | 8 |
| M | 3 | 18 |
| N | 4 | 32 |
So, K is the first shell or orbit that can hold up to 2 electrons, L is the 2nd shell which can hold up to 8 electrons, M is the third shell that can hold up to 18 electrons, and N is the fourth shell that can hold up to 32 electrons.
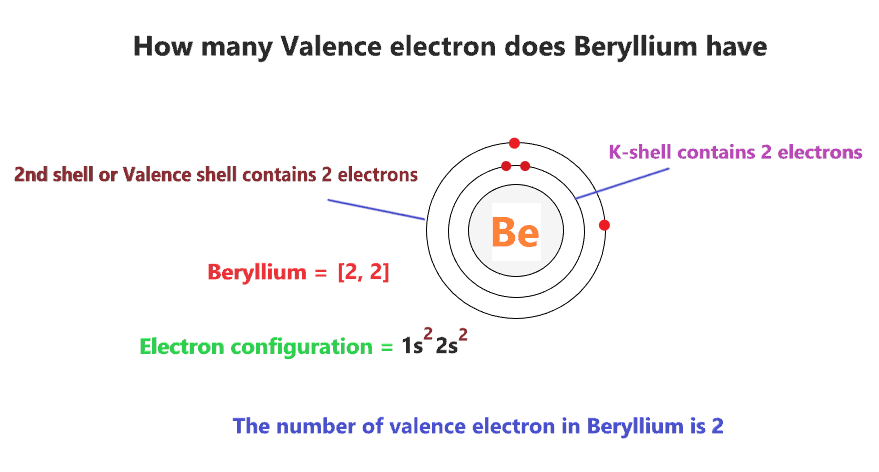
Now, Beryllium has an atomic number of 4 and it contains a total number of 4 electrons. Hence, 2 electrons will go in the first shell(K), and the remaining two electrons will go in the second shell(L).
Therefore, the electrons per shell for Beryllium is 2, 2, hence, we can say, based on the shell, the electronic configuration of the Beryllium atom is [2, 2].
Also check – How to draw Bohr model of Beryllium atom
Beryllium Valence electrons
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom. They have more energy, hence, they are part of most chemical reactions.
We can find valence electrons of an atom either by knowing its periodic group number or its electron configuration. Both these ways are super easy.
Finding Beryllium Valence electrons through the Group number
For neutral atoms, the valence electrons of an atom will be equal to its main periodic group number. However, for transition metals, the process of finding valence electrons is complicated.
Now, for determining the valence electron for the Beryllium atom, look at the periodic table and find its Group number. The group number can be found from its column on the periodic table.

So, the number of valence electrons in Beryllium is 2. Since it belongs to Group 2nd in the Periodic table.
Finding Beryllium Valence electrons through the Electron configuration or Bohr model
We know, the electron configuration of the Beryllium atom is 1s22s2, and valence electrons are those electrons found in the outer shell of an atom.
This electron configuration of Beryllium shows that the outer shell of Beryllium has 2 electrons(2s2), hence, the number of valence electrons in the Beryllium atom is 2.
Also, we know, that the electron configuration of Beryllium based on the shells is [2, 2], which means, the two electrons are present in the first shell, and the next two electrons are present in 2nd shell or outer shell.
Hence, the electrons found in the 2nd shell of the Beryllium atom are its valence electrons because it is the outermost shell also called the valence shell.
The 2nd shell or outer shell of the Beryllium atom contains 2 electrons, therefore, the number of valence electrons in the Beryllium atom is 2.
Check – Valence electron calculator to calculate the number of valence electrons for any atom
Electron configuration, Valence electrons, and Orbital diagram of Beryllium in tabular form
| Name of atom | Beryllium (Be) |
| Number of electrons | 4 |
| Number of electrons per shell | [2, 2] |
| Number of valence electrons | 2 |
| Electron configuration | 1s22s2 or [He] 2s2 |
| Orbital diagram | Consists of two orbitals – 1s and 2s. |
Also read:
- Nitrogen orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Oxygen orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Carbon orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Fluorine orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Neon orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Boron orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Sodium orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Magnesium orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Aluminum orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Silicon orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Phosphorous orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Sulfur orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Chlorine orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Argon orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Potassium orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Calcium orbital diagram and electron configuration
- Lithium orbital diagram and electron configuration
FAQ
What are the Ground state and Excited-state Electron configurations of Beryllium?There is a simple difference between Ground state and Excited-state configuration. The ground state configuration of an atom is the same as its regular electron configuration in which electrons remain in the lowest possible energy. So, the ground-state electron configuration for the Beryllium atom is 1s22s2. The excited-state configuration of an atom is different from the regular configuration of an atom, this occurs, when an electron is excited and jumps into a higher orbital. The excited-state electron configuration for Beryllium is 1s22s12p1. |
What is the shorthand electron configuration of Beryllium?The shorthand electron configuration for the Beryllium atom is [He] 2s2. ∴ [He] electron configuration is 1s2. |
Which element has the 1s22s2 Electron configuration?Element with electron configuration 1s22s2 is Beryllium (Be) that has the atomic number of 4. |
How many valence electrons does Beryllium have?The Beryllium atom has 2 valence electrons in its outermost or valence shell. Beryllium is belonged to group 2nd and has the atomic number of 4. |
What is the orbital diagram for Beryllium (Be)?The orbital diagram for Beryllium is drawn with 2 orbitals. The orbitals are 1s and 2s. The Beryllium orbital diagram contains 2 electrons in 1s orbital and the remaining 2 electrons in 2s orbital. The orbital diagram for a ground-state electron configuration of the Beryllium atom is as follows –
|
What is the electron configuration of the Be2+ ion?We know, in general, that the electron configuration of Beryllium (Be) is 1s22s2. Now, in the Be2+ ion, the positive charge means, Beryllium loses two electrons. Therefore, to write the electron configuration of the Be2+ ion, we have to remove two electrons from the configuration of Beryllium (Be). ∴ The resulting electron configuration for the Beryllium ion (Be2+) will be 1s2. It resembles the configuration of the nearest inert gas i.e Helium. |
Properties of Beryllium
- It has a hexagonal closed-packed crystal structure.
- It has a 1.57 electronegativity.
- It has a boiling point of 2469 °C and a melting point of 1287 °C.
- It appears as white-gray metallic and lightweight in nature.
- It is one of the rare elements in the universe.
- The oxidation state of beryllium is +2.
Summary
- The electron configuration of Beryllium in terms of the shell or orbit is [2, 2].
- The ground-state electron configuration of the Beryllium (Be) atom is 1s22s2. And for the excited state, it is 1s22s12p1.
- The shorthand electron configuration for Beryllium is [He] 2s2.
- The electron configuration for the Be2+ is 1s2.
- The number of valence electrons available for Beryllium atoms is 2. Beryllium is situated in Group 2nd and has an atomic number of 4.
- The first shell of Beryllium has 2 electrons and the outer shell or valence shell of Beryllium has also 2 electrons, hence, the number of valence electrons in the Beryllium atom is 2.
- The orbital diagram for Beryllium is drawn by following three principles – the Aufbau principle, Hund’s principle, and Pauli’s exclusion principle.
- The Beryllium orbital diagram comprises two orbitals. The two orbitals are 1s and 2s.
- The first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital and the remaining two electrons in the 2s orbital.
About the author
Vishal Goyal is the founder of Topblogtenz, a comprehensive resource for students seeking guidance and support in their chemistry studies. He holds a degree in B.Tech (Chemical Engineering) and has four years of experience as a chemistry tutor. The team at Topblogtenz includes experts like experienced researchers, professors, and educators, with the goal of making complex subjects like chemistry accessible and understandable for all. A passion for sharing knowledge and a love for chemistry and science drives the team behind the website. Let's connect through LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vishal-goyal-2926a122b/