List of orbital diagrams for all elements of the periodic table |Diagram + Chart|
The orbital diagram or orbital notation simply represents the arrangement of electrons in different orbitals of an atom. In an orbital diagram, an electron is represented by an arrow, while a box represents an atomic orbital.
Here is the list of all elements (1 to 118) in the periodic table with their orbital diagram.
Orbital diagram for all elements (1-118)
Atomic no. | Orbital diagram for all elements |
1 | Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H)[1]
|
2 | Orbital diagram of Helium (He)[2]
|
3 | Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li)[2, 1]
|
4 | Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be)[2, 2]
|
5 | Orbital diagram of Boron (B)[2, 3]
|
6 | Orbital diagram of Carbon (C)[2, 4]
|
7 | Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N)[2, 5]
|
8 | Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O)[2, 6]
|
9 | Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F)[2, 7]
|
10 | Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne)[2, 8]
|
11 | Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na)[2, 8, 1]
|
12 | Orbital diagram of Magnesium (Mg)[2, 8, 2]
|
13 | Orbital diagram of Aluminum (Al)[2, 8, 3]
|
14 | Orbital diagram of Silicon (Si)[2, 8, 4]
|
15 | Orbital diagram of Phosphorus (P)[2, 8, 5]
|
16 | Orbital diagram of Sulfur (S)[2, 8, 6]
|
17 | Orbital diagram of Chlorine (Cl)[2, 8, 7]
|
18 | Orbital diagram of Argon (Ar)[2, 8, 8]
|
19 | Orbital diagram of Potassium (K)[2, 8, 8, 1]
|
20 | Orbital diagram of Calcium (Ca)[2, 8, 8, 2]
|
21 | Orbital diagram of Scandium (Sc)[2, 8, 9, 2]
|
22 | Orbital diagram of Titanium (Ti)[2, 8, 10, 2]
|
23 | Orbital diagram of Vanadium (V)[2, 8, 11, 2]
|
24 | Orbital diagram of Chromium (Cr)[2, 8, 13, 1]
|
25 | Orbital diagram of Manganese (Mn)[2, 8, 13, 2]
|
26 | Orbital diagram of Iron (Fe)[2, 8, 14, 2]
|
27 | Orbital diagram of Cobalt (Co)[2, 8, 15, 2]
|
28 | Orbital diagram of Nickel (Ni)[2, 8, 16, 2]
|
29 | Orbital diagram of Copper (Cu)[2, 8, 18, 1]
|
30 | Orbital diagram of Zinc (Zn)[2, 8, 18, 2]
|
31 | Orbital diagram of Gallium (Ga)[2, 8, 18, 3]
|
32 | Orbital diagram of Germanium (Ge)[2, 8, 18, 4]
|
33 | Orbital diagram of Arsenic (As)[2, 8, 18, 5]
|
34 | Orbital diagram of Selenium (Se)[2, 8, 18, 6]
|
35 | Orbital diagram of Bromine (Br)[2, 8, 18, 7]
|
36 | Orbital diagram of Krypton (Kr)[2, 8, 18, 8]
|
37 | Orbital diagram of Rubidium (Rb)[2, 8, 18, 8, 1]
|
38 | Orbital diagram of Strontium (Sr)[2, 8, 18, 8, 2]
|
39 | Orbital diagram of Yttrium (Y)[2, 8, 18, 9, 2]
|
40 | Orbital diagram of Zirconium (Zr)[2, 8, 18, 10, 2]
|
41 | Orbital diagram of Niobium (Nb)[2, 8, 18, 12, 1]
|
42 | Orbital diagram of Molybdenum (Mo)[2, 8, 18, 13, 1]
|
43 | Orbital diagram of Technetium (Tc)[2, 8, 18, 13, 2]
|
44 | Orbital diagram of Ruthenium (Ru)[2, 8, 18, 15, 1]
|
45 | Orbital diagram of Rhodium (Rh)[2, 8, 18, 16, 1]
|
46 | Orbital diagram of Palladium (Pd)[2, 8, 18, 18]
|
47 | Orbital diagram of Silver (Ag)[2, 8, 18, 18, 1]
|
48 | Orbital diagram of Cadmium (Cd)[2, 8, 18, 18, 2]
|
49 | Orbital diagram of Indium (In)[2, 8, 18, 18, 3]
|
50 | Orbital diagram of Tin (Sn)[2, 8, 18, 18, 4]
|
51 | Orbital diagram of Antimony (Sb)[2, 8, 18, 18, 5]
|
52 | Orbital diagram of Tellurium (Te)[2, 8, 18, 18, 6]
|
53 | Orbital diagram of Iodine (I)[2, 8, 18, 18, 7]
|
54 | Orbital diagram of Xenon (Xe)[2, 8, 18, 18, 8]
|
55 | Orbital diagram of Cesium (Cs)[2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 1]
|
56 | Orbital diagram of Barium (Ba)[2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 2]
|
57 | Orbital diagram of Lanthanum (La)[2, 8, 18, 18, 9, 2]
|
58 | Orbital diagram of Cerium (Ce)[2, 8, 18, 19, 9, 2]
|
59 | Orbital diagram of Praseodymium (Pr)[2, 8, 18, 21, 8, 2]
|
60 | Orbital diagram of Neodymium (Nd)[2, 8, 18, 22, 8, 2]
|
61 | Orbital diagram of Promethium (Pm)[2, 8, 18, 23, 8, 2]
|
62 | Orbital diagram of Samarium (Sm)[2, 8, 18, 24, 8, 2]
|
63 | Orbital diagram of Europium (Eu)[2, 8, 18, 25, 8, 2]
|
64 | Orbital diagram of Gadolinium (Gd)[2, 8, 18, 25, 9, 2]
|
65 | Orbital diagram of Terbium (Tb)[2, 8, 18, 27, 8, 2]
|
66 | Orbital diagram of Dysprosium (Dy)[2, 8, 18, 28, 8, 2]
|
67 | Orbital diagram of Holmium (Ho)[2, 8, 18, 29, 8, 2]
|
68 | Orbital diagram of Erbium (Er)[2, 8, 18, 30, 8, 2]
|
69 | Orbital diagram of Thulium (Tm)[2, 8, 18, 31, 8, 2]
|
70 | Orbital diagram of Ytterbium (Yb)[2, 8, 18, 32, 8, 2]
|
71 | Orbital diagram of Lutetium (Lu)[2, 8, 18, 32, 9, 2]
|
72 | Orbital diagram of Hafnium (Hf)[2, 8, 18, 32, 10, 2]
|
73 | Orbital diagram of Tantalum (Ta)[2, 8, 18, 32, 11, 2]
|
74 | Orbital diagram of Tungsten (W)[2, 8, 18, 32, 12, 2]
|
75 | Orbital diagram of Rhenium (Re)[2, 8, 18, 32, 13, 2]
|
76 | Orbital diagram of Osmium (Os)[2, 8, 18, 32, 14, 2]
|
77 | Orbital diagram of Iridium (Ir)[2, 8, 18, 32, 15, 2]
|
78 | Orbital diagram of Platinum (Pt)[2, 8, 18, 32, 17, 1]
|
79 | Orbital diagram of Gold (Au)[2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 1]
|
80 | Orbital diagram of Mercury (Hg)[2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 2]
|
81 | Orbital diagram of Thallium (Tl)[2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 3]
|
82 | Orbital diagram of Lead (Pb)[2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 4]
|
83 | Orbital diagram of Bismuth (Bi)[2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 5]
|
84 | Orbital diagram of Polonium (Po)[2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 6]
|
85 | Orbital diagram of Astatine (At)[2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 7]
|
86 | Orbital diagram of Radon (Rn)[2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8]
|
87 | Orbital diagram of Francium (Fr)[2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8, 1]
|
88 | Orbital diagram of Radium (Ra)[2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8, 2]
|
89 | Orbital diagram of Actinium (Ac)[2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 9, 2]
|
90 | Orbital diagram of Thorium (Th)[2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 10, 2]
|
91 | Orbital diagram of Protactinium (Pa)[2, 8, 18, 32, 20, 9, 2]
|
92 | Orbital diagram of Uranium (U)[2, 8, 18, 32, 21, 9, 2]
|
93 | Orbital diagram of Neptunium (Np)[2, 8, 18, 32, 22, 9, 2]
|
94 | Orbital diagram of Plutonium (Pu)[2, 8, 18, 32, 24, 8, 2]
|
95 | Orbital diagram of Americium (Am)[2, 8, 18, 32, 25, 8, 2]
|
96 | Orbital diagram of Curium (Cm)[2, 8, 18, 32, 25, 9, 2]
|
97 | Orbital diagram of Berkelium (Bk)[2, 8, 18, 32, 27, 8, 2]
|
98 | Orbital diagram of Californium (Cf)[2, 8, 18, 32, 28, 8, 2]
|
99 | Orbital diagram of Einsteinium (Es)[2, 8, 18, 32, 29, 8, 2]
|
100 | Orbital diagram of Fermium (Fm)[2, 8, 18, 32, 30, 8, 2]
|
101 | Orbital diagram of Mendelevium (Md)[2, 8, 18, 32, 31, 8, 2]
|
102 | Orbital diagram of Nobelium (No)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 8, 2]
|
103 | Orbital diagram of Lawrencium (Lr)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 8, 3]
|
104 | Orbital diagram of Rutherfordium (Rf)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 10, 2]
|
105 | Orbital diagram of Dubnium (Db)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 11, 2]
|
106 | Orbital diagram of Seaborgium (Sg)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 12, 2]
|
107 | Orbital diagram of Bohrium (Bh)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 13, 2]
|
108 | Orbital diagram of Hassium (Hs)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 14, 2]
|
109 | Orbital diagram of Meitnerium (Mt)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 15, 2]
|
110 | Orbital diagram of Darmstadtium (Ds)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 16, 2]
|
111 | Orbital diagram of Roentgenium (Rg)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 17, 2]
|
112 | Orbital diagram of Copernicium (Cn)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 2]
|
113 | Orbital diagram of Nihonium (Nh)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 3]
|
114 | Orbital diagram of Flerovium (Fl)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 4]
|
115 | Orbital diagram of Moscovium (Mc)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 5]
|
116 | Orbital diagram of Livermorium (Lv)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 6]
|
117 | Orbital diagram of Tennessine (Ts)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 7]
|
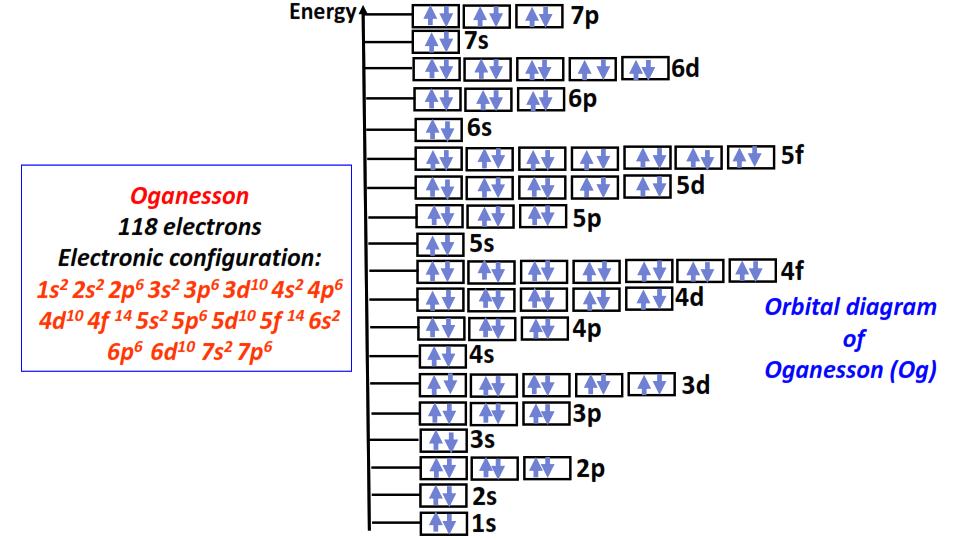
118 | Orbital diagram of Oganesson (Og)[2, 8, 18, 32, 32 18, 8]
|
That’s all, This is the list of Orbital diagrams for each element of the Periodic table. Also, if you find difficulty in drawing the Orbital diagram for any elements, then go through the links given below to understand the process of drawing the Orbital diagram in detail.
Go through the links to understand the process of drawing the Orbital diagram:-
- Nitrogen orbital diagram
- Oxygen orbital diagram
- Carbon orbital diagram
- Fluorine orbital diagram
- Neon orbital diagram
- Boron orbital diagram
- Sodium orbital diagram
- Magnesium orbital diagram
- Aluminum orbital diagram
- Silicon orbital diagram
- Phosphorous orbital diagram
- Sulfur orbital diagram
- Chlorine orbital diagram
- Argon orbital diagram
- Potassium orbital diagram
- Calcium orbital diagram
- Beryllium orbital diagram
- Lithium orbital diagram
- Scandium orbital diagram
- Titanium orbital diagram
- Vanadium orbital diagram
Also check:
FAQ
What is an Orbital diagram? |
| An orbital diagram, or orbital filling diagram, is a type of notation that illustrates an atom’s electron distribution and electron spin within orbitals. |
How can you draw the Orbital diagram for each element of the Periodic table? |
To draw the orbital diagram for an atom, follow these basic steps.
|
Reference
- Wikipedia, (n.d.). Electron configurations of the elements (data page). [online] Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electron_configurations_of_the_elements_(data_page) [Accessed 13-09-2023].
About the author
Vishal Goyal is the founder of Topblogtenz, a comprehensive resource for students seeking guidance and support in their chemistry studies. He holds a degree in B.Tech (Chemical Engineering) and has four years of experience as a chemistry tutor. The team at Topblogtenz includes experts like experienced researchers, professors, and educators, with the goal of making complex subjects like chemistry accessible and understandable for all. A passion for sharing knowledge and a love for chemistry and science drives the team behind the website. Let's connect through LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vishal-goyal-2926a122b/