Is Soap an acid or base or neutral?

Soap is one of the products that we use every day for a variety of cleansing, washing, bathing, and other household works. Soap is used as a component of some lubricant and it is very helpful in removing oil, dirt, and some types of microorganisms by denaturing their proteins.
In this article, we will discuss Is Soap an acid or base/alkaline? Nature of its solution, etc.
Is Soap an acid or base?
Soap is a basic salt, a combination of a weak acid (fatty acids) and a strong base (lye). It is made by the reaction of long-chain fatty acids with a strong base like sodium hydroxide (NaOH). The majority of soaps have a pH value within the range of 9-10 which shows their slightly basic nature in solution.
Let’s read in detail, How does Soap behave as basic salt? Why it is not acidic? etc.
| Name of Molecule | Soap |
| General formula | RCOO–Na+ |
| Prepared by | Saponification reaction |
| Nature | Alkaline or Basic salt |
Why Soap is basic salt?
Have you ever heard what do these terms mean by “Acidic salt”, “Basic salt”?
Acidic salt: It has a pH value of less than 7. Acidic salt is formed when a neutralization reaction carries out between strong acid and weak base. Examples of acidic salt – NH4Cl, NH4NO3, NH4Br, etc.
Also Read:-
Basic salt: These salt have a pH value of more than 7. A basic salt is formed when a neutralization reaction carries out between a strong base and weak acid. Examples of basic salt – are NaCN, Na2CO3, NaF, etc.
Also Read:-
Ok, Now come to the point Why does Soap act as basic salt?
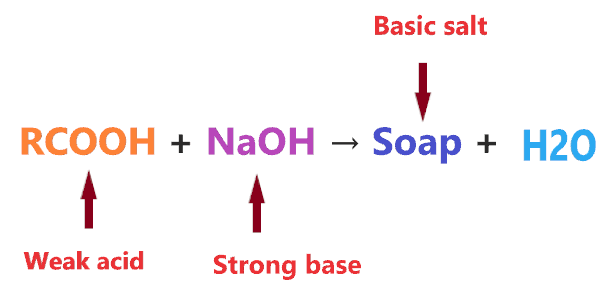
- Soap is made by heating fatty acids such as carboxylic acid which is a weak organic acid with strong bases like sodium hydroxide(NaOH).
- The metal hydroxide like NaOH is a very strong alkaline or base in nature whereas all organic acids are weak as they don’t dissociate completely in an aqueous solution.
- As per the concepts of salts, a combination of a strong base and weak acid leads to the formation of basic salt.
In short, Soaps are basic or alkali because they are the salt of weak acids and a strong base.
Why Soap is not acidic or neutral salt?
A neutral salt means showing no effect of acidic or alkaline properties when dissolved in water and an acidic salt means having more properties of acid when dissolved in an aqueous solution with a pH value of less than 7.
The important concept of acid-base strength–
- A stronger base + weaker acid forms a basic aqueous solution due to the presence of more OH– ions. (OH– > H+)
- Stronger acid + weaker base forms an acidic aqueous solution due to the presence of more H+ ions. (H+ > OH–)
- Stronger/weaker acid + Stronger/weaker base forms a neutral aqueous solution due to the presence of the same number of OH– and H+ in the solution. (H+ = OH–)

So, Why the Soap solution is not acidic or neutral in nature? As Soap is a salt of a weak acid and strong base, so, its ions undergo hydrolysis to yield more OH– ions as compared to H+ ions.
When Soap(RCOONa) is dissolved in water, it dissociates into two ions RCOO– and Na+
⇒ RCOONa → RCOO– + Na+
The Na+ is a cation of strong base (NaOH), hence, it will not undergo hydrolysis in water and doesn’t affect the pH of the solution. But the RCOO– is the anion of a weak acid that gets hydrolysis in water to form (RCOOH), leaving OH– ions that make the solution basic.
⇒ RCOO– + H2O → RCOOH + OH–
RCOOH is a weak acid that mostly remain undisscociated in solution causes fewer H+ ions.
So, we can say the presence of a large number of OH– ions than H+ ions in solution due to the hydrolysis of RCOO– ions, Soaps are basic or alkaline in nature instead of acidic or neutral.
Also read:–
How Soaps solution are basic in nature?
A solution having a pH value of more than 7 is called a basic solution.
Note: A solution nature depends on the H+ and OH– ions. When more OH– ions are present in a solution, then the solution becomes basic, and when more H+ ions are present in a solution, the solution becomes acidic.
Let’s see How Soaps solution is basic instead of acidic?
Soaps are denoted by the general formula RCOONa that is made by heating weak fatty acid(RCOOH) with a strong base(NaOH), this is also called saponification reaction.
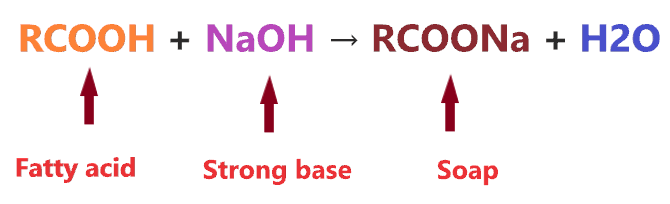
Ok, We prepare the soap(RCOONa) but how can we explain its basic nature? To do this we have to simply understand the hydrolysis reaction of soap.
When soap undergoes in water solution, it dissociates into two ions(RCOO– and Na+), the RCOO– is a conjugate base anion of weak organic acid and Na+ is a conjugate acid of strong base(NaOH).
Na+ is a very weak conjugate acid, hence, it is not able to react either with H+ or OH– in water solution, you can assume it as a spectator ion because it is almost useless as it doesn’t take part in any chemical reaction, so leave it aside.
RCOO– is a conjugate base of a weak acid and is able to take part in the chemical reaction. According to the Bronsted-Lowry base theory, a base is a substance that can accept the proton from another compound.
So, RCOO– is a base that accepts the H+ ions and is converted into RCOOH which is a weak acid.
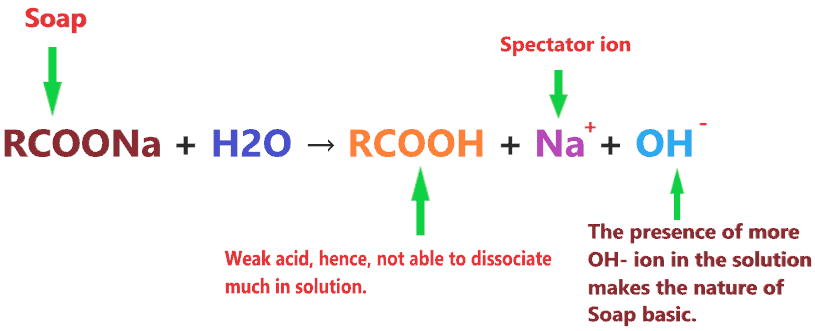
Now, it’s very straightforward, when Soap(RCOONa) undergoes an aqueous solution, the RCOO– accepts the H+ ions and converted into RCOOH which is a weak acid, hence, it will not dissociate much or just partially dissociate, so, a large number of H+ ions are absorbed by the RCOO–, causes fewer H+ ions in the final solution.
Whereas Na+ is useless as it is only a spectator ion, so, the OH– ions are leftover everywhere in the solution of soap which is the most appropriate reason for its basic nature.
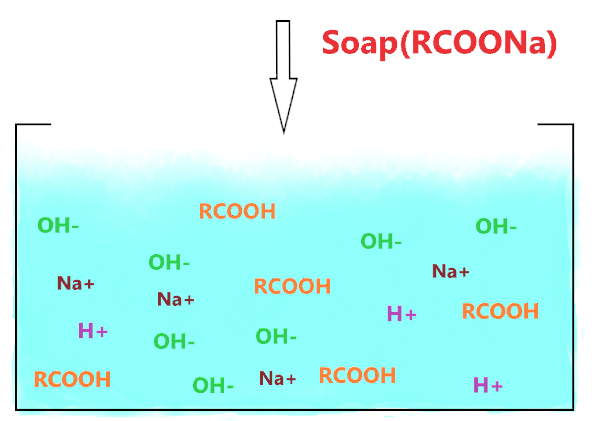
The above picture shows the final aqueous solution of soap. Cleary, it shows there is a large number of OH– ions present everywhere because of the hydrolysis of RCOO– ions(RCOO– + H2O → RCOOH + OH–) whereas fatty acids(RCOOH) are just weak acid that partially dissociates and liberates fewer H+ ions, most of them are absorbed by the RCOO– ion and leftover H+ ions present in very small quantity as compare to OH– ions.
Therefore, the presence of more OH– ions raises the pH value of a soap solution and makes it basic or alkaline in nature.
Is hand or liquid soap also basic?
Soaps are actually sodium or potassium salts of long-chain fatty acids or carboxylic acids which are prepared by the saponification reaction that involves the heating of a strong base like potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide(NaOH) with a long-chain fatty acid that is weak in nature.
Liquid soaps are usually potassium salts of fatty acids and solid or hand soaps are usually sodium salt of fatty acids.
So, it doesn’t matter whether the soap is in liquid form or another form, whatever, it will show basic behavior with a pH value around 8-10.
Also, the taste of soap appears bitter which implies that the base has a bitter taste as well.
Also Check:
Types of Soaps
Soaps are divided into different categories based on their appearance or uses.
1. Liquid soaps = Liquid soaps are usually potassium salts of fatty acids and it is made with the hot process method. More water is added in the process of making these types of soaps.
2. Toilet soaps = It is used for household and personal cleaning. It is prepared by saponification of triglycerides with sodium hydroxide(NaOH).
3. Glycerine soaps = These soaps contain glycerin, a component of fat or oil. “Glycerin soap is made by melting and continuously heating soap that has been partially dissolved in a high-percentage alcohol solution until the mixture reaches a clear, jelly-like consistency.”
And many more Soaps like Medicated soap, Beauty soap, Kitchen soap, Laundry soap, Transparent soap.
Benefits of Soap
- Soaps are used as cleansers and lubricants.
- It reduces the infection caused by dirt microorganisms.
- Soap is cheaper and has high antibacterial properties.
- It is used in the hospital for the prevention of transmission of infection from patients to health workers.
- It also emulsifies oils.
Summary
- Is Soap acidic or basic or neutral? Soap is an alkali salt or basic salt. It is made by heating fatty acids (weak acid) with strong bases (lye). The resulting product of this combination forms alkanol (usually glycerin) and salt with a basic pH.
- When soap solution drop is put on a red litmus paper, it will change into blue that implies, soap solutions are alkaline in nature.
- The solution of soap is alkaline in nature. Because, in its aqueous solution, a large number of OH– ions are present due to the hydrolysis of RCOO– ions(RCOO– + H2O → RCOOH + OH–). Hence, soap with water has a pH value of above 7, usually near 8-10.
- The soap solution is not acidic because fatty acids are weak acid which doesn’t dissociate much, so, only a small number of H+ ions are liberated in the solution, and most of them are absorbed by the RCOO– ions which are later converted into RCOOH, hence, in the solution of soap, not much freely H+ ions are present and this makes it non-acidic in nature.
- Soaps are water-soluble sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids which are formed by the saponification reaction between strong bases and fatty acids.
- Fatty acids typically have 12 to 18 carbon atoms.
About the author
Vishal Goyal is the founder of Topblogtenz, a comprehensive resource for students seeking guidance and support in their chemistry studies. He holds a degree in B.Tech (Chemical Engineering) and has four years of experience as a chemistry tutor. The team at Topblogtenz includes experts like experienced researchers, professors, and educators, with the goal of making complex subjects like chemistry accessible and understandable for all. A passion for sharing knowledge and a love for chemistry and science drives the team behind the website. Let's connect through LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vishal-goyal-2926a122b/