Is Potassium bromide (KBr) an acid or base or salt?

Potassium bromide is also known as a bromide salt of potassium appears as a white crystalline solid with a pungent bitter saline taste. It has a chemical formula KBr. It is freely soluble in water and widely used as a sedative and as an anticonvulsant.
In this article, we will study Is Potassium bromide (KBr) is an acid or base or neutral salt?
So, Is KBr an acid or base? KBr is a neutral salt as it is made from the neutralization reaction of the strong acid (HBr) with a strong base (KOH). The pH value of the aqueous solution of KOH is 7. Because strong acid and a strong base will neutralize each other effects and a neutral solution forms.
| Name of Molecule | Potassium bromide |
| Chemical formula | KBr |
| Molar mass | 119.002 g·mol−1 |
| Nature | Neutral salt |
| pH | 7 |
Why KBr is not acidic in nature?
As we know, the acid compound has a pH value of less than 7 and they release H+ ions whenever dissolved in an aqueous solution. In short, an acidic compound is a proton donor which increases the concentration of hydrogen ions in the final solution.
In the case of KBr, it is not considered an acid because it doesn’t have any H+ or proton ion to donate. So, on dissolving KBr in an aqueous solution, it doesn’t induce any effect i.e. Aqueous solution remains the same as before, after dissolving KBr.
Let’s elaborate more on why KBr doesn’t hold the property of acidic with the help of two acid-base theories (a). Arrhenius acid theory (b). Bronsted-Lowry acid theory.
(a). Arrhenius acid theory
According to Arrhenius’s theory of acid ” A compound is said to be acid when added in water, it increases the number of H+ ions in solution.
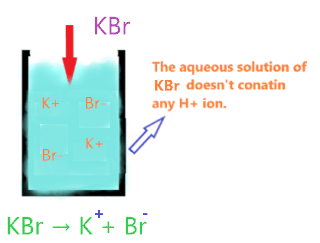
Now, KBr on dissolving in aqueous solution, split into two ions K+ and Br–. As we see, it doesn’t have any H+ ion to donate.
Hence, KBr is not qualified as Arrhenius acid as its aqueous solution doesn’t contain any H+ ions.
(b). Bronsted-Lowry acid theory
This theory is an enhanced version of Arrhenius’s theory given for acid-base.
Bronsted-Lowry acid theory state that a compound having the ability to donate the proton to another compound is categorized as Bronsted-Lowry acid.
Since KBr doesn’t have any proton to donate. So, we can say KBr is neither Arrhenius acid nor Bronsted-Lowry acid as per their acidic theories.
Why KBr is not base in nature?
The species having a pH value of more than 7 are said to be basic in nature or “A base is any substance that increases the concentration of OH– ion in aqueous solution”.
Or you can say a base is a compound that accepts hydrogen ions or protons.
So, in the case of KBr, as like acidic component(H+), it doesn’t have OH– ion also, therefore, dissolving in an aqueous solution does not alter the nature of the solution i.e. it remains the same as before.
As per Bronsted-Lowry base theory, a compound is said to be base when it makes conjugate acid by accepting one proton from other species, or as per Arrhenius base theory, a compound produces OH– ion in an aqueous solution.
“Conjugate acid is formed when one proton is added to parent base”.
Since KBr doesn’t have the ability to accept the proton from other species, it cannot make any conjugate acid, nor it produce OH– ions in an aqueous solution.
Therefore, we can say, KBr is not a Bronsted-Lowry base as per its theory.
Why KBr is neutral salt?
A neutral salt means showing no effect of acidic or alkaline properties when dissolved in water.
Or neutral salt is a salt resulting from the neutralization between acid and base having neither acidic nor alkaline properties when dissolved in an aqueous solution.
A neutralization simply means the interaction of acid and base to form the water molecule and salt compound.

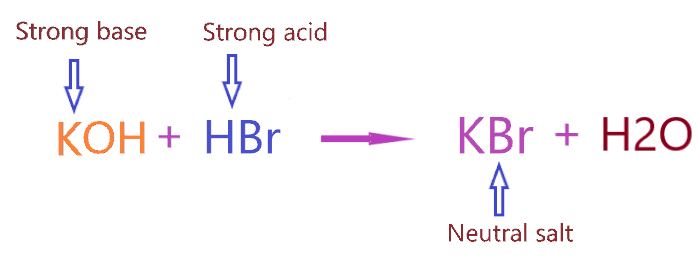
Now let’s come to the point Why KBr is neutral salt? As we know KBr salt is formed when the strong base (KOH) and strong acid (HBr) react with each other. Or you can say KBr salt formed by the neutralization reaction carries between HBr acid and KOH base.
⇒ KOH + HBr → KBr + H2O
Also Read:-
As per the concept of the neutralization reaction-
⇒ Strong base + Weak acid = Basic solution
⇒ Stronger acid + Weak base = Acidic solution
⇒ Strong acid + Strong base = Neutral solution
That means the interaction of strong base and weak acid forms a basic solution, stronger acid with weak base forms an acidic solution, and stronger acid with stronger base forms a neutral solution.
As we discussed, KBr is formed when strong acid(HBr) reacts with a strong base(KOH). Hence, as per the above concepts, when a neutralization reaction carries between a strong acid and strong base, it will form neutral salt having a pH value equal to 7.
Using the ionic reaction of potassium bromide formation we can also understand why the aqueous solution of KBr is considered neutral.
We know KBr is formed when KOH reacts with the HBr.
⇒ KOH + HBr → KBr + H₂O
The ionic reaction of the above reaction can be written as-
⇒ K+ + OH– + H+ + Br– → K+ + Br– + H2O
Common ions from both(left and right sides) should be canceled out of each other.
Remaining ions we get-
⇒ OH– + H+ → H2O
∴ The final solution of KBr contains an equal number of H+ and OH–, therefore, its aqueous solution is neutral.
Also, The ions of KBr, K+ is the very weak conjugate acid of KOH, and Br– is a very weak conjugate base of HBr, hence, both these ions are very weak in nature, therefore, the effect of these ions on altering the pH value of the aqueous solution is almost zero.
The conjugate acid of KOH is K+ which is too weak to function as an acid in water. The conjugate base of HBr is Br– which is too weak to function as a base in water.
This reason can also be considered for explaining why the aqueous solution of potassium bromide (KBr) is neutral with no acidic or alkaline properties.
Some examples of neutral salt – NaNO3, NaCl, KNO3, KBr, NaBr, etc.
Also Read:
Some examples of acidic salt – NH4NO3, NH4Br, NH4Cl, etc.
Also Read:-
Some examples of basic salt – Na2CO3, NaF, NaCN, Soap, etc.
Also Read:-
The pH value of potassium bromide
“pH is a measure of hydrogen ion(H+) and hydroxide ion(OH–) concentration in aqueous solution.
Since the water solution of potassium bromide neither contains H+ ion nor hydroxide ion, so there is no effect on its pH value.
Also, the dissociation of KBr into K+ and Br– ion in water solution have no effect on altering the pH value.
Therefore, the pH value of a water solution of potassium bromide is 7.
Also Check:
Uses of Potassium bromide
- It is widely used as an anticonvulsant and a sedative.
- It is used as an antiepileptic medication for dogs.
- It is used in the water treatment of aquariums.
- It is used to manufacture different types of chemicals.
- It is also used in photography and optics.
Properties of Potassium bromide
- It has a melting point of 734 °C and a boiling point of 1,435 °C.
- It is soluble in water but not soluble in acetonitrile.
- At very high concentrations, potassium bromide tastes bitter and salty.
- It is generally odorless in nature.
- It is an ionic salt with a pH value equal to near 7.
Summary
Potassium bromide has a saline taste and appears as a white crystalline solid having a molar mass of 119.002 g·mol−1. It is one of the important metal halides used as a sedative. At last, Overview of this article on “Is KBr an acid or base or neutral salt?”
- Is Potassium bromide (KBr) an acid or base or salt? KBr is a neutral salt. It is formed from the neutralization reaction carried out between strong acid, namely Hydrobromic acid (HBr), and strong base, namely Potassium hydroxide (KOH).
- The pH value of potassium bromide is 7.
- Potassium bromide (KBr) is neither held acidic properties nor alkaline. Because of the absence of the two most important ions needed for acid and base nature, that is H+ and OH–.
About the author
Vishal Goyal is the founder of Topblogtenz, a comprehensive resource for students seeking guidance and support in their chemistry studies. He holds a degree in B.Tech (Chemical Engineering) and has four years of experience as a chemistry tutor. The team at Topblogtenz includes experts like experienced researchers, professors, and educators, with the goal of making complex subjects like chemistry accessible and understandable for all. A passion for sharing knowledge and a love for chemistry and science drives the team behind the website. Let's connect through LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vishal-goyal-2926a122b/