Is Water (H2O) an acid or base or neutral? - It's Conjugate acid and Conjugate base

Water is one of the important fluids for all living things on earth. It is tasteless, colorless, and odorless having the chemical formula H2O. At standard temperature and pressure, the liquid state of H2O is known as water. Almost 70% of the earth is covered by water in the form of oceans and seas. Water also exists in form of ice and steam vapor.
In this article, we will discuss Is Water (H2O) is an acid or base? It’s conjugate acid as well as conjugate base, etc.
So, Is H2O an acid or base? Water(H2O) is amphoteric, which means it can act as an acid as well as base, depending on what it is reacting with.
But the extremely pure water is always neutral(neither acidic nor basic) since it contains an equal number of H+ ions and OH– ions and pH equal to 7.
Let’s discuss in more detail how can H2O can act as an acid as well as a base?
| Name of Molecule | Water |
| Chemical formula | H2O |
| Molar mass | 18.01 g mol−1 |
| Nature | Amphoteric |
| The conjugate acid of H2O | H3O+ |
| The conjugate base of H2O | OH– |
Why water (H2O) act as acid?
To get a better perspective of the acidic nature of H2O. We first look at what the term “Acid” means.
Acid is generally a compound that has a pH value of less than 7 and contains one or more replaceable hydrogen ions. When acidic compounds are dissolved in an aqueous solution, they will release H+ ions.
So, now Why does H2O act as an acid? H2O can act as acid only in one condition when the reacting compound is more basic than it e.g. NaOH, KOH, NH3. This is because a stronger base has more ability to “accept the proton”.
Hence, H2O has to donate the proton when reacting with a strong base, and anything that donates the proton is considered acid in nature.
H2O act as acid when reacting compound have smaller Ka than it.
⇒ Ka for H2O = 1 × 10-14
⇒ Ka for NH3 = 1 × 10-35
So, reacting compound(NH3) have smaller Ka, hence, here, H2O will act as acid.
Therefore, when H2O reacted with a stronger base than it such as NaOH, NH3, etc. then it left with no choice and have to release proton.
Let’s consider the example of H2O + NH3 for understanding why H2O(water) acts as the acid in presence of a stronger base.
Note: NH3 is not the strongest base, in fact, it is a weak base in nature but it is more basic than H2O because oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen, hence, it less inclined to donate the electron pair compare to nitrogen. And this makes, water less basic than ammonia.
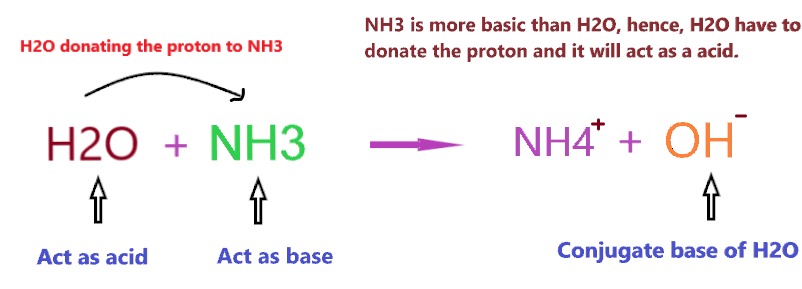
As we see in the above reaction, H2O reacts with a stronger base(NH3) than it, therefore, donating one proton to NH3 and making a conjugate base(OH–).
The Bronsted-Lowry theory for acid said that “the acid is the substance that donates the proton to reacting species and itself makes a conjugate base.”
As we see in the above figure, H2O is donating the proton to NH3 and making a conjugate base(OH–).
Therefore, we can say H2O (water) acts as Bronsted-Lowry acid if reacting compound is a stronger base than it.
Also check:-
Why water (H2O) act as base?
A base is defined as a proton acceptor or electron-pair donor. A stronger base liberates more OH– when dissolved in an aqueous solution and has a pH value of more than 7.
So, Why does H2O act as a base? H2O acts as a base when reacting with the compound that is more acidic than it, i.e. HCl, HNO3, H2SO4, etc. This is because a stronger acid has more ability to “donate the proton”.
Hence, H2O has to accept the proton when reacting with a strong acid, and anything that accepts the proton is considered base in nature.
H2O act as base when reacting compound have larger Ka than it.
⇒ Ka for H2O = 1 × 10-14
⇒ Ka for HCl = 1.3 × 106
So, reacting compound(HCl) have larger Ka, hence, here, H2O will act as base.
Therefore, when H2O reacts with stronger acid like HCl, it is left with no choice and has to accept the proton from HCl. And we know anything that accepts the proton act as a base.

As we see in the above reaction, H2O reacts with a stronger acid(HCl), therefore, accepting one proton from HCl and making a conjugate acid(H3O+).
As per Bronsted-Lowry base theory, a compound is said to base when it accepts the proton from reacting species and forms a conjugate acid.
Therefore, we can say H2O can act as a Bronsted-Lowry base if react with strong acid.
Also read:-
Is Water (H2O) neutral?
Neutral means the compound neither has acidic properties nor basic properties and pH is equal to 7.
Pure water is neutral because it contains an equal number of H+ and OH– ions in the solution.
- When H+ > OH– then the aqueous solution is acidic.
- When OH– > H+ then the aqueous solution is basic.
- When H+ = OH– then the aqueous solution is neutral.
Generally, we can’t say H2O is absolute acid or base or neutral in nature as it totally depends on to whom it reacts.
- If the reacting compound is a strong base, then water will act as an acid.
- If the reacting compound is a strong acid, then water will act as a base.
- If there is no reacting compound, the medium is an only a pure solution, then water is considered neutral with a pH value equal to 7
Some examples of neutral compounds – are NaNO3, NaCl, KCl, KNO3, etc.
Also Read:-
What is the conjugate base and conjugate acid of H2O (Water)?
To know what is the conjugate acid-base of H2O, first, we have to through the concept of conjugate acid-base pairs.
The concept of conjugate acid-base pair.
- A very strong acid always forms a weak conjugate base.
- A very strong base always forms a weak conjugate acid.
- A very weak acid always forms a strong conjugate base.
- A very weak base always forms a strong conjugate acid.
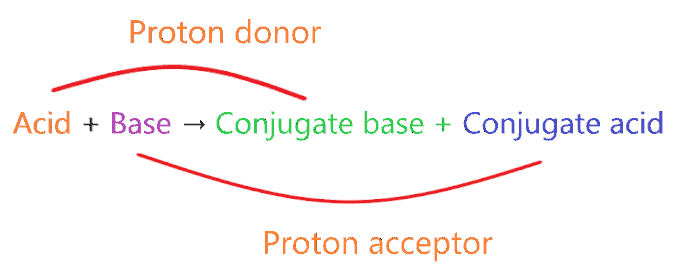
Conjugate acid:-
A conjugate acid is a species formed by gaining one electron by base compound or you can say when the proton is added to the parent base then the compound is formed which is called conjugate acid. Example of conjugate acid-
⇒ NH3 + H+ → NH4+
Here in this reaction, NH3 is a weak base that accepts the proton when dissolved in an aqueous solution and forms conjugate acid(NH4+).
So, NH4+ is the strong conjugate acid of NH3.
Conjugate base:-
A conjugate base is a species formed by losing one electron by an acid compound or you can say when the proton is removed from the parent acid then the compound is formed which is called the conjugate base. Examples of conjugate base-
⇒ HCl → H+ + Cl–
Here, in this reaction, HCl is a strong acid that donates the proton when dissolved in an aqueous solution and formed a conjugate base(Cl–).
So, Cl– is the weak conjugate base of HCl.
⇒ H2SO4 → H+ + HSO4–
Here, in this reaction, H2SO4 is a strong acid that donates the proton when dissolved in an aqueous solution and formed a conjugate base(HSO4–).
So, HSO4– is a weak conjugate base of H2SO4.
Now, what is the conjugate acid and base of H2O? When H2O acts as an acid it will make a conjugate base and when it acts as the base it will make conjugate acid.
⇒ When H2O reacts with a stronger base than it such as NH3, it donates the one proton to NH3 and formed a conjugate base (OH-).
⇒ When H2O reacts with stronger acid than it such as HCl, it accepts the one proton from HCl and formed a conjugate acid(H3O+).
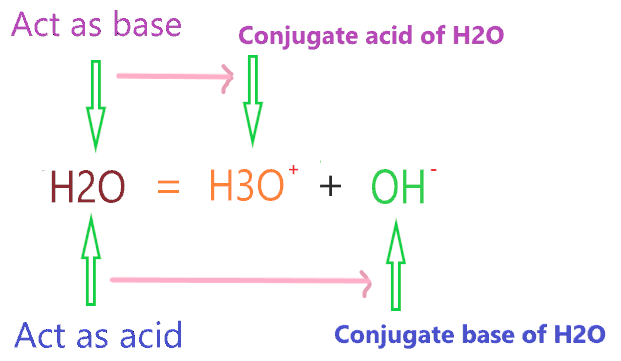
∴ The conjugate acid of H2O is hydronium ion(H3O+) and the conjugate base is hydroxyl ion(OH–).
Uses of Water
- Water is the most essential liquid for all living things on earth and is used to eliminate dehydration.
- It is used to generate electricity in power plants.
- It is used in agriculture operations in form of irrigation.
- It is used to regulate body temperature.
- It is used to mix cement and concrete.
- It is used for washing purposes.
- Water helps improve the circulation of oxygen throughout the body.
- Water is almost in all industrial applications.
Properties of Water
- The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom in H2O at an angle of 104.5°.
- The molar mass of water is 18.01528 g/mol.
- The boiling point of water is 100°C.
- Water is a universal solvent as almost all substances such as acids, bases, salts, and sugar are readily dissolved in it.
- Water is a colorless, tasteless, and odorless liquid.
- It is found in all three states – solid, liquid, and gases.
- Water (H2O) is a polar compound.
- Water becomes less dense as it freezes.
- It has low electrical conductivity.
- Water is a neutral substance and has a pH value equal to 7.
Also Read:- Is H2O ionic or covalent?
Summary
- The conjugate acid of H2O is hydronium ion(H3O+).
- The conjugate base of H2O is a hydroxyl ion(OH–).
- Is water (H2O) acid or base? H2O (Water) is both an acid and base. Since it can act as an acid in presence of a strong base and act as a base in presence of strong acid.
- In presence of a strong base like NaOH, KOH, NH3, etc. the H2O will act as an acid.
- In presence of a strong acid like HCl, HNO3, H2SO4, etc. the H2O will act as a base.
- But H2O can never be both acid or base at the same time.
- We can’t say H2O (water) is absolute acid or base or neutral in nature as it totally depends on whom it reacts. If there is no reacting compound or medium is only a pure solution, then water(H2O) can be considered neutral.
About the author
Vishal Goyal is the founder of Topblogtenz, a comprehensive resource for students seeking guidance and support in their chemistry studies. He holds a degree in B.Tech (Chemical Engineering) and has four years of experience as a chemistry tutor. The team at Topblogtenz includes experts like experienced researchers, professors, and educators, with the goal of making complex subjects like chemistry accessible and understandable for all. A passion for sharing knowledge and a love for chemistry and science drives the team behind the website. Let's connect through LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vishal-goyal-2926a122b/