Is Ca(OH)2 an acid or base? Weak or Strong - Calcium hydroxide

Calcium hydroxide is white in color appears as a granular solid that has no odor with the chemical formula Ca(OH)2. It is also known as slaked lime. It is produced when calcium oxide is mixed with water. It is poorly soluble in water.
In this article, we will discuss Is Calcium hydroxide (CaOH2) is acid or base? Is it strong or weak, etc?
So, Is Ca(OH)2 an acid or base? Ca(OH)2 is a base. In an aqueous solution, it dissociates into two ions (Ca2+ and 2OH–), the presence of OH– ions in the aqueous solution of Ca(OH)2 makes it basic in nature.
| Name of Molecule | Calcium hydroxide |
| Chemical formula | Ca(OH)2 |
| pH value | Around 12 |
| Nature | Strong base |
| Basicity (pKb) | 1.37 (first OH–), 2.43 (second OH–) |
Why Ca(OH)2 is base?
A base is defined as a proton acceptor or lone pair donor. When Ca(OH)2 dissolved in water, it split into two ions Ca2+ and 2OH–.
As Ca(OH)2 dissociates into Ca2+ and 2OH-, this OH– ion accepts the proton (H+) to form water.
⇒ Ca(OH)2 + (aq) → Ca2+ (aq) + 2OH– (aq)
Also, as per Arrhenius’s base theory, a compound is said to be base when it produces OH- ion through ionization or through dissociation in water.
Clearly, When Ca(OH)2 is dissolved in water, it produces two hydroxide ions per molecule. Hence, we can say Ca(OH)2 is a base or Arrhenius base in nature.
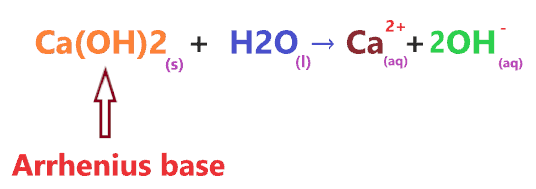
Is Ca(OH)2 strong base or weak base?
To know whether Ca(OH)2 is a strong base or weak, you must know the basic difference between a strong base and a weak base.
Strong base: A compound is a strong base when it completely dissociates in an aqueous solution and liberates a large number of hydroxide ions. All moles of the strong base dissociates into hydroxide ion(OH–) and no part remains undissociated in the solution.
Example: Sodium hydroxide(NaOH), Barium hydroxide (Ba(OH)2), Lithium hydroxide (LiOH), Potassium hydroxide (KOH), etc.
Also Read:-
- Is NaOH a strong or weak base?
- Is KOH a strong or weak base?
- Is LiOH a strong or weak base?
- Is Ba(OH)2 a strong or weak base?
Weak base: A compound is a weak base when it partially or not completely dissociates in an aqueous solution. It means only some parts of the weak base dissociate in the solution to give OH– ion but some parts remain undissociated inside the solution.
Example- Ammonia (NH3), Methylamine (CH3NH2), NH4OH, etc.
Also Read:-
| Strong base | Weak base |
| They ionize completely. | They do not completely ionize. |
| They are highly reactive. | They are less reactive compare to a strong base. |
| The value of pH lies between 10 to 14. | The value of pH lies between 7 to 10. |
| They have a high equilibrium constant. | They have a less equilibrium constant. |
| They are good electrolytes. | They are not so good electrolytes compared to a strong base. |
| Example – NaOH, KOH, LiOH, etc. | Example – N2H4, NH3, NH4OH, etc. |
So, Is Calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 strong base or a weak base? Ca(OH)2 is the strong base. Because it completely dissociates in an aqueous solution to yield OH– ion and no moles of it remain undissociated inside the solution. And the amount of OH– ions in an aqueous solution is very high and we know OH– ions have a tendency to accept the proton.
So, more proton acceptors present in the solution ultimately make Ca(OH)2 a strong base.
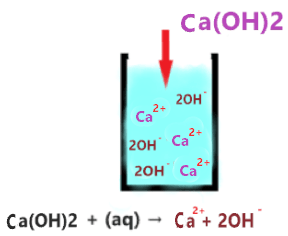
As you see in the above aqueous solution when Ca(OH)2 is dissolved in water, it is completely ionized into the ions(Ca2+ and 2OH–). No undissociated molecule(Ca(OH)2) is present in the solution, only ionized ions are present everywhere in the solution.
The single arrow used in the above reaction shows that only forward reaction takes place at equilibrium and no backward reaction occurs in solution.
As Ca2+ is a very weak conjugate acid of Ca(OH)2, hence it has no ability to react with either OH– ion or with water molecules ions. Thus, only splitting ions(Ca2+ and 2OH–) remain in the solution.
Or you can also assume the Ca2+ as a spectator ion because it is almost useless in solution, it has no effect on the pH value of the solution.
“A spectator ion is an ion that does not take part in the chemical reaction and is found in solution both before and after the reaction.”
Hence, a large number of hydroxide ions present in the aqueous solution of Ca(OH)2, steadily increase the pH value and rises the effect of the basic in the solution.
Also, the base dissociation constant value(Kb) for Ca(OH)2 is larger than 1.
An base dissociation constant (Kb) is a quantitative measure of the strength of an base in solution.
⇒ If the value of the dissociation constant of the base is greater than 1 (Kb > 1), then the nature of the compound is a strong base.
⇒ If Kb < 1, then the nature of the compound is a weak base.
So, the higher the value of the base dissociation constant, the larger is the strength of a base in solution.
Here’s the list of some common strong/weak acids and bases.

Also check:-
How to know if Ca(OH)2 is acid or base practically?
To know if compound acid or base practically, one of the easiest ways to use litmus paper.
“Litmus is a water-soluble mixture of different dyes extracted from lichens. It is often absorbed onto filter paper to produce one of the oldest forms of pH indicator, used to test materials for acidity.”
Note: When Red litmus paper turns blue then the compound is said to be base. And when blue litmus paper turns red then the compound is said to be acidic.
When Ca(OH)2 is contacted with red litmus paper then litmus paper turns into blue color. So, we can say Ca(OH)2 is the base.
Is Ca(OH)2 alkali or not?
Alkali is a strong base that produces hydroxide ions when it is dissolved in water. All soluble hydroxides like lithium, cesium, sodium, potassium, etc. are alkali metals.
An alkali is said to be strongest when it produces almost all OH– ions when it is dissolved in water. As Ca(OH)2 molecule, when dissolved in water produce almost all OH– ions that ultimately make it strong alkali.
Uses of Calcium hydroxide
- It is used as the precursor to other calcium compounds.
- It is used to clarify raw juice from sugarcane in the sugar industry.
- It is used as a pH modifier.
- It is also used in the treatment of sewage water as a clarifying agent.
- It is used in the production of many plastics.
Properties of Calcium hydroxide
- It is white in color and appears as a granular solid.
- It has a melting point of 580 °C.
- It has a hexagonal crystal structure.
- It is non-flammable.
-
The pH of Calcium Hydroxide is around 12.
Summary
- Is Ca(OH)2 acid or base? Ca(OH)2 is base, not an acid. Because it dissociates into OH– ions in an aqueous solution which quickly absorbs H+ to form a water molecule.
- Ca(OH)2 acts as Arrhenius base, According to the Arrhenius theory, the compound is said to be base when it produces OH– ion through ionization and increases the concentration of OH– ions in an aqueous solution.
- Is Ca(OH)2 weak or strong base? Ca(OH)2 is the strong base, since, it completely dissociates in an aqueous solution and produces a higher amount of OH– ions.
- Calcium hydroxide in an aqueous solution can provide two hydroxide ions per molecule.
- The base dissociation constant value for Ca(OH)2 is larger than 1.
About the author
Vishal Goyal is the founder of Topblogtenz, a comprehensive resource for students seeking guidance and support in their chemistry studies. He holds a degree in B.Tech (Chemical Engineering) and has four years of experience as a chemistry tutor. The team at Topblogtenz includes experts like experienced researchers, professors, and educators, with the goal of making complex subjects like chemistry accessible and understandable for all. A passion for sharing knowledge and a love for chemistry and science drives the team behind the website. Let's connect through LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vishal-goyal-2926a122b/

Better