Is formic (HCOOH) an acid or base? Weak or Strong - Conjugate base

Formic acid appears as the colorless fuming liquid is the simplest carboxylic acid that contains one carbon with the chemical formula CH2O2 or HCOOH. It has a strong odor of pungent and a molar mass of 46.02 g·mol−1.
In this article, we will discuss Is HCOOH an acid or base? Is it strong or weak in nature? Its conjugate acid-base pairs, etc.
So, Is HCOOH an acid or base? HCOOH is considered an acid. It releases H+ ions when dissolved in an aqueous solution. And acid is a substance that donates the proton to other compounds or releases H+ ions in a water solution. Therefore, HCOOH is acid, since it releases H+ ions in a water solution. It has a pH value of 2.38 in 0.10 M solution.
| Name of Molecule | Formic acid |
| Chemical formula | HCOOH |
| Molar mass | 46.02 g/mol |
| Conjugate base | HCOO- |
| Nature | Weak acid |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.74 |
Why HCOOH is acid?
An acid is a substance that liberates an H+ ion or proton when dissolved in water and having a pH value from 1 to 6.
So, HCOOH is considered an acid because when it is dissolved in water or in an aqueous solution then it dissociates into two parts (HCOO– and H+), the presence of H+ ion in the aqueous solution of HCOOH makes it acid in nature.
⇒ HCOOH ⇌ H+ + HCOO−
To understand whether HCOOH is an acid or base, look out for the two important theories of the acid-base concept (a). Arrhenius theory (b). Bronsted-Lowry theory
1. Arrhenius’s theory for acid:
According to Arrhenius’s theory for acid, the substance which produces an H+ ion or proton on dissolving in an aqueous solution is categorized as an acid. So, when HCOOH is dissolved in an aqueous solution then it produces some H+ ion or proton in the solution.
Therefore, we can say HCOOH is acid as per Arrhenius’s theory of acid-base pair.
2. Bronsted-Lowry theory for acid:
According to Bronsted-Lowry’s theory for acid, the substance which donates the proton to other compounds and itself makes a conjugate base categorized as an acid. So, when HCOOH reacted with water, it donates the proton or H+ ion and itself makes a conjugate base(HCOO–).
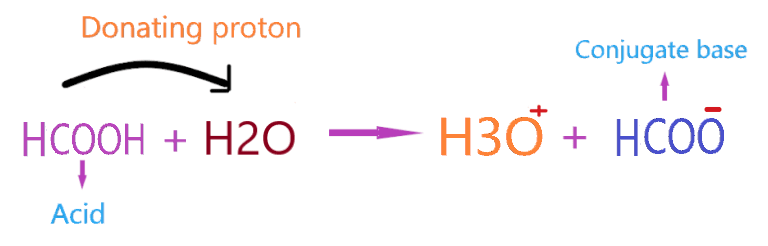
As you see in the above reaction, HCOOH liberates or donates the one H+ ion to the water molecule and itself makes a conjugate base (HCOO–). The final aqueous solution of HCOOH contains H3O+ ions and a conjugate base(HCOO–).
Therefore, we can say HCOOH acts as Bronsted-Lowry acid because of proton donating ability when reacting with a compound such as H2O.
Note:- Bronsted-Lowry theory is not limited to an aqueous solution, this theory state that a substance is said to be Bronsted-Lowry acid when it donates the proton to other reacting species, the reacting species should be base or very less acidic in nature because according to this theory-
A substance can function as an Bronsted-Lowry acid only in the presence of a base. i.e. OH–, NaOH, NH3, H2O, etc.
But Arrhenius’s theory said a substance is an acid when it loses the proton on dissolving in an aqueous solution. The presence of water solution is a must for knowing the acidic nature of the substance according to Arrhenius’s theory.
Is HCOOH strong acid or weak acid?
For knowing whether formic acid is strong or weak, look out for the basic difference between a strong acid and weak acid-
A strong acid is a compound that is 100% ionized or completely dissociates in a solution and gives a high amount of hydrogen ions. It means all the moles of acid will dissociate to give H+ ions and no undissociated acid remains in the solution. They have a low pH value and good electrical conductivity properties.
Examples of strong acids: Hydrochloric acid(HCl), Sulfuric acid(H2SO4), Nitric acid(HNO3), HBr, HI, etc.
Also Read:-
- Is H2SO4 a strong acid?
- Is HNO3 a strong acid?
- Is HCl a strong acid?
- Is HI a strong acid?
- Is HClO4 a strong acid?
- Is HBr a strong acid?
And weak acid is a compound that partially dissociates which means not all moles of weak acid dissociate in a solution to give H+ ion or they are not 100 % ionized in a solution and give only a low amount of hydrogen ions. They have a high pKa or pH value with moderate electrical conductivity property and weak electrolyte compared to strong acid.
Examples of a weak acids – Hydrogen fluoride(HF), Ammonium ion(NH4+), Phosphoric acid(H3PO4), Acetic acid(CH3COOH), etc.
Also Read:
- Is CH3COOH a weak acid?
- Is HF a weak acid?
- Is HCN a weak acid?
- Is HNO2 a weak acid?
- Is H3PO4 a weak acid?
- Is H2CO3 a weak acid?
- Is NH4+ a weak acid?
Now, Is formic acid (HCOOH) strong or weak? HCOOH is a weak acid. Because it partially dissociates in an aqueous solution or it does not ionize completely in solution to produce H+ ions. The strength of an acid depends on its ability to ionize completely or partially in a solution.
So, all molecules of formic acid not ionized completely cause fewer hydrogen ions in the aqueous solution and we know the more the hydrogen ion present in the solution, the higher will be the acidic strength of that solution.
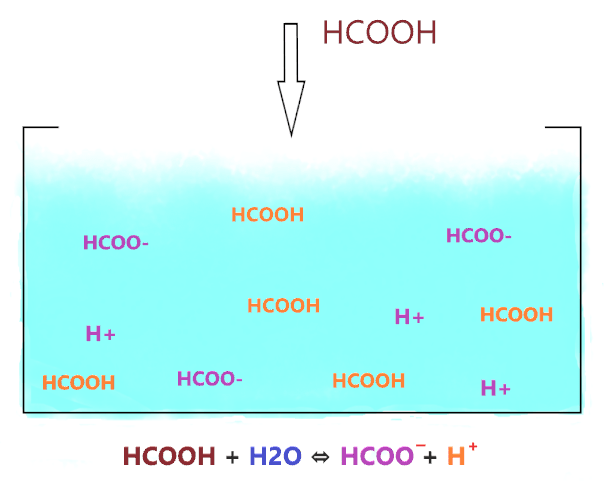
As shown in the figure, when HCOOH is dissolved in water, it dissociates into two ions (HCOO– and H+) but the ion(HCOO–) is not stable in ionic form, it wants to combine with H+ and make HCOOH again.
So, not all the HCOOH molecules dissociate, most of them stay together and only a few of them dissociate and liberate H+ ions.
Also, the double arrow in the reaction of formic acid(HCOOH) and water(H2O) shows that both forward and backward reactions occur at equilibrium.
The acid dissociation constant value for formic acid(HCOOH) is 1.8 × 10-4 and anything less than 1 value of the acid dissociation constant for the molecule shows the weakly acidic nature.
Note:- In weak acid, the backward is more dominating than forwarding reaction, as the splitting ions easily react with each other to reform the acid molecule.
Also Read:
Here’s the list of some common acids and bases with their strength.

Why HCOOH is not a base?
A base is a substance that accepts the proton from other compounds or releases OH– ion in an aqueous solution. The strength of basicity in an aqueous solution depends on the number of OH– ions in the solution.
So, HCOOH is not a base because when it is dissolved in water, it produces an H+ ion instead of an OH– ion. Also, HCOOH is a proton donor which is also against the property of the base.
⇒ HCOOH + (aq) → H+ (aq) + HCOO– (aq)
Here’s what Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry said for base compound-
Arrhenius’s theory for base:
According to the Arrhenius theory for the base, the substance which produces an OH- ion on dissolving in an aqueous solution is categorized as a base. HCOOH doesn’t liberate any OH– ion when dissolved in water, so it does not fall into the category of Arrhenius bases.
Bronsted-Lowry theory for base:
According to the Bronsted-Lowry theory for the base, the substance which accepts the proton to other compounds and itself makes a conjugate acid categorized as a base. So, when HCOOH is treated with the water molecule, it donates the proton to the water molecule and itself makes a conjugate base.
Therefore, HCOOH also does not fall into the category of Bronsted-Lowry bases.

What is the Conjugate base of HCOOH?
When one proton loses from acid then a compound is formed which is called the conjugate base of that acid, similarly when one proton is added to the base then a compound is formed which is called conjugate acid of that base. In technical terms, Compounds differentiated from each other by a single proton(H+) are said to be Conjugate acid-base pairs.
The concept of conjugate acid-base pair.
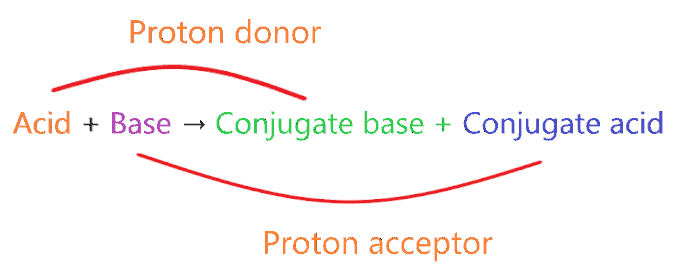
- A very strong acid always forms a weak conjugate base.
- A very strong base always forms a weak conjugate acid.
- A very weak acid always forms a strong conjugate base.
- A very weak base always forms a strong conjugate acid.
So, HCOOH is a weak acid that forms a conjugate base according to the concept of conjugate acid-base pair.
The conjugate base of HCOOH is the formate ion(HCOO-).
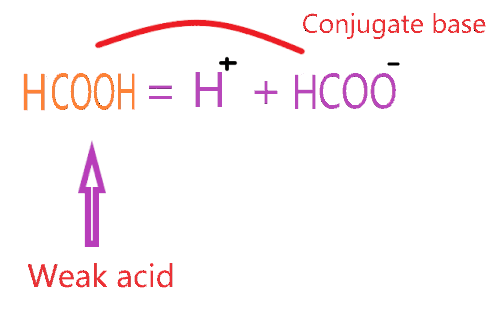
Uses of formic acid
- It is used as a preservative and antibacterial agent in livestock feed.
- It has a role as an antibacterial agent.
- It is used as a reducing agent.
- It is also used for the treatment of warts.
- It is used in a fuel cell also.
Summary
- Is HCOOH an acid or base? HCOOH is an acid. Because on dissociation in an aqueous solution, it liberates the H+ ion showing its acidic nature.
- HCOOH is acting as an Arrhenius acid and Bronsted-Lowry acid.
- The conjugate base of Formic acid (HCOOH) is the Formate ion (HCOO–).
- The pKa value for Formic acid (HCOOH) is 3.74.
- HCOOH is a weak acid. Because it contains fewer hydrogen ions in the aqueous solution since it only dissociates partially or is not 100% ionized when dissolved in water.
- The Ka value for formic acid is 1.8 × 10-4 which is way lower than recommended value for a strong acid(Ka > 1), hence, HCOOH is a weak acid.
About the author
Vishal Goyal is the founder of Topblogtenz, a comprehensive resource for students seeking guidance and support in their chemistry studies. He holds a degree in B.Tech (Chemical Engineering) and has four years of experience as a chemistry tutor. The team at Topblogtenz includes experts like experienced researchers, professors, and educators, with the goal of making complex subjects like chemistry accessible and understandable for all. A passion for sharing knowledge and a love for chemistry and science drives the team behind the website. Let's connect through LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vishal-goyal-2926a122b/