Is HClO3 a strong acid? – Chloric acid strong or weak
Chloric acid is an important oxo-acid of chlorine represented by the chemical formula HClO3. It appears as a colorless liquid at room temperature. HClO3 is a strong oxidizing agent and is corrosive to tissue and metals. It is also known to increase the burning of combustible materials.
Many students have a query regarding the acidic strength of the chloric acid (HClO3) molecule, i.e., is it strong or weak?
In this article, we will answer that question and discuss the acidic strength of the HClO3 molecule.
So, is HClO3 a strong acid or weak?
Chloric acid (HClO3) is a strong acid. It completely dissociates into H+ and ClO3– ions when dissolved in an aqueous solution.
The conjugate base (ClO3–) of chloric acid is highly stable due to the strong delocalization of the negative charge. The high oxidation number (+5) of the central Cl atom in the chloric acid (HClO3) molecule leads to a weak O-H bond.
Hence, as HClO3 removes the proton (H+) quickly, it is a strong acid with a Ka value greater than 1.
| Name of molecule | Chloric acid |
| Chemical formula | HClO3 |
| Molar mass | 84.45 g mol−1 |
| Nature | Strong acid |
| Conjugate base | ClO3– |
| Ka value | >>1 |
Why is HClO3 an acid?
To know why HClO3 is acting as an acid? We have to look into the theories of acids and bases. One of them is Arrhenius’s acid-base theory.
This theory states that a compound is acidic if it produces H+ ions when dissolved in an aqueous solution and forms H3O+ ions when combined with water.
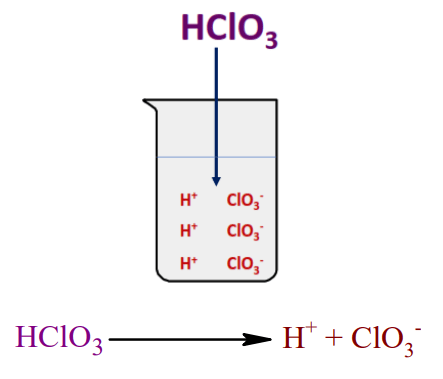
HClO3 dissociates in an aqueous solution to produce H+ and ClO3–.
![]()
Then, the proton (H+) combines with a water molecule and forms H3O+.
![]()
Also, according to Arrhenius, an acid is a compound that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution.
In the case of the HClO3, it liberates H+ ions, increasing the concentration of hydrogen ions in the aqueous solution.
So, the HClO3 follows all conditions needed for the Arrhenius acid. Hence, HClO3 is an Arrhenius acid.
Now we look for another important acid-base theory, the Bronsted-Lowry theory.
This theory states that a compound is an acid if it donates a proton to other species and forms a conjugate base. In short, a Bronsted-Lowry acid is a proton (H+) donor.
Let’s check whether or not HClO3 fulfills the requirement for classifying as Bronsted-Lowry acid.
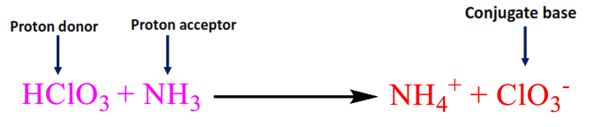
Consider the reaction of HClO3 reacting with NH3.
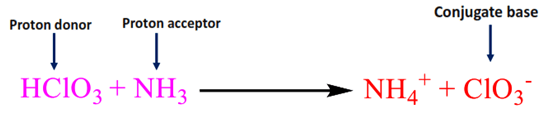
Here, HClO3 reacts with NH3 and donates the proton, forming a ClO3– conjugate base.
HClO3 acts as Bronsted-Lowry acid as it donates the proton and forms a conjugate base.
Chlorate ion (ClO3–) is the conjugate base of the acid HClO3.
Is HClO3 a strong or weak acid?
An acid that easily releases H+ ions and dissociates completely in a solution is called a strong acid. Some examples of strong acids are HCl, HClO4, HI, H2SO4, etc.
Properties of strong acid:-
- They are strong electrolytes and have high conductivity.
- Their pH value lies between 1 to 3.
- They dissociate completely and release many H+ ions in a solution.
In contrast, an acid that does not release H+ ions quickly and only partially dissociates in a solution is called a weak acid. Some examples of weak acids are CH3COOH, H3PO4, HF, etc.
Properties of weak acids:-
- They are weak electrolytes and have less conductivity than strong acids.
- Their pH value lies between 3 to 7.
- They show partial ionization to produce H+ in a solution.
Now, Is HClO3 a strong or weak acid? HClO3 is a strong acid. The following factors will explain the strength of chloric acid (HClO3):
- Ionization in aqueous solution
- Acid dissociation constant (Ka)
- Strength of O-H bond
- Stability of the conjugate base
Ionization in aqueous solution
An acid that completely dissociates (100% ionized) in a solution is strong.
HClO3 is a strong acid because it completely ionizes in an aqueous solution producing H+ and ClO3–. All the parts completely break off and are ionized in an aqueous solution.
As on dissolving HClO3 in an aqueous solution, no parts of H+ remain bound to it, which means the concentration of hydrogen ion increased in the solution. Hence, we can say HClO3 is a strong acid.
Acid dissociation constant (Ka)
The strength of an acid can also be calculated by another factor known as the acid dissociation constant (Ka).
The acid dissociation constant (Ka) is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in a solution.
Acids with a constant dissociation value greater than 1 are considered strong acids.
Chloric acid (HClO3) also has a large acid dissociation constant (Ka) value ( Ka = >> 1).
The high Ka value indicates that chloric acid (HClO3) is strong.
Strength of O-H bond
The strength of the O-H bonds can also determine the strength of oxoacids.
The strength of the O-H bonds is directly related to the oxidation number of the central atom in oxoacids. The higher the oxidation state of the central atom is, the weaker the O-H bond is.
As a result, the acid with a weaker O-H bond will be stronger as H+ ions will be released easily.
In HClO3, the central atom (Cl) is surrounded by three O-atoms and has an oxidation state of +5. Consequently, it can release H+ ions due to the weaker O-H bond. Hence, HClO3 is a strong acid.
Stability of the conjugate base
The acidic strength of an acid is directly related to the strength of its conjugate base. The higher the stability of the conjugate base, the stronger will be the acidic strength of the compound.
Due to the strong delocalization of the negative charge, the conjugate base of the chloric acid, i.e., ClO3–, is highly stabilized.
As a result, chloric acid (HClO3) is a strong acid.
Properties of chloric acid (HClO3)
- Chloric acid is a strong acid.
- The molar mass of chloric acid is 84.45 g/mol.
- It is a strong oxidizing agent.
- It is extremely corrosive to tissues and metals.
- It appears as a colorless solution at room temperature.
Also, check –
- How to tell if an acid or base is strong or weak?
- How to tell if something is an acid or base?
- Is HClO4 an acid or base? – Strong or weak
- Is HNO2 an acid or base? – Strong or weak
- Is HNO3 an acid or base? – Strong or weak
FAQ
Is chloric acid (HClO3) strong or weak? |
| Chloric acid (HClO3) is a strong acid. |
Which is more acidic, HClO3 or HClO4? |
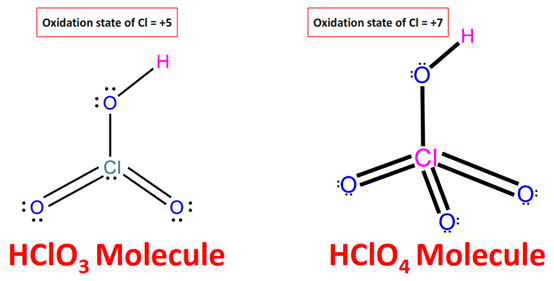
The strength of an acid can be compared by the relative ease with which it releases the proton (H+ ion), which in turn depends on the strength of the O-H bonds in the oxoacids like HClO4 and HClO3. The higher the oxidation state of the central atom is, the weaker the O-H bond is. The oxidation number of chlorine in HClO4 and HClO3 is +7 and +5, respectively. As a result, due to a weaker O-H bond in the perchloric acid (HClO4), it will release H+ ions more easily. Consequently, HClO4 is stronger than HClO3.
|
Which is more acidic, HClO3 or HClO2? |
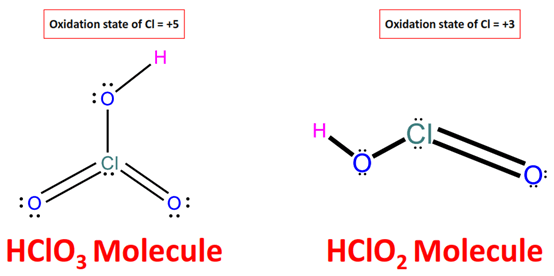
The higher the oxidation state of the central atom in the oxoacids, the higher the acidic strength is. The reason is that the tendency of acid to release an H+ unit increases with the oxidation state due to the resulting decrease in the strength of O-H bonds. The oxidation number of chlorine in HClO3 and HClO2 is +5 and +3, respectively. As a result, due to a weaker O-H bond in the chloric acid (HClO3), it will release H+ ions more easily. Hence, HClO3 is stronger than HClO2.
|
Summary
- HClO3 is an acid. It liberates the H+ ions when dissolved in the solution, increasing the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution.
- The conjugate base of HClO3 is a chlorate ion (ClO3–). It is formed after removing one proton from chloric acid (HClO3).
- Chloric acid is a strong acid. It completely dissociates into H+ and ClO3– ions in an aqueous solution.
- The conjugate base (ClO3–) of chloric acid is highly stable due to the strong delocalization of the negative charge.
- The high oxidation number (+5) of the central Cl atom in the chloric acid (HClO3) molecule leads to a weak O-H bond.
- In conclusion, as HClO3 removes the proton (H+) quickly, it is a strong acid with a high Ka value of approx 103.
References
- “Chloric acid” Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chloric_acid.
- “Table of Acids with Ka’s and pKa’s” (PDF). The University of California Santa Barbara. [Online]. Available: https://clas.sa.ucsb.edu/staff/Resource%20Folder/Chem109ABC/Acid,%20Base%20Strength/Table%20of%20Acids%20w%20Kas%20and%20pKas.pdf.
About the author
Vishal Goyal is the founder of Topblogtenz, a comprehensive resource for students seeking guidance and support in their chemistry studies. He holds a degree in B.Tech (Chemical Engineering) and has four years of experience as a chemistry tutor. The team at Topblogtenz includes experts like experienced researchers, professors, and educators, with the goal of making complex subjects like chemistry accessible and understandable for all. A passion for sharing knowledge and a love for chemistry and science drives the team behind the website. Let's connect through LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vishal-goyal-2926a122b/