OH- and H+ Calculator
The formulas to calculate H+ and OH– from the pH and pOH value is –
∴ [H+] = 10-pH and [OH–] = 10-pOH
[H+] and [OH-] Calculator
[OH-] =
Step by Step Solution:
Step 1: Understand that the pH and pOH of a solution are related by the equation:
pH + pOH = 14
This relationship is true at 25°C, a standard temperature for these sorts of calculations.
Step 2: Calculate the pH from the given pOH value:
pOH is given as , therefore:
pH = 14 - pOH = 14 - =
Step 2: Use the pH and pOH value to determine the concentrations of H+ and OH- ions:
The formulas to calculate the H+ and OH- concentrations are:
[H+] = 10-pH
[OH-] = 10-pOH
Substitute the pH and pOH values:
[H+] = 10- = M
[OH-] = 10- = M
Step 4: Conclude the results:
The concentration of H+ ions is M, and the concentration of OH- ions is M.
How to use H+ and OH– calculators?
Using the above calculator, you can easily calculate the concentrations of H+ and OH– ions in the solution.
- Enter either pH or pOH value in the input field labeled.
- Click the “Calculate” button.
- The results for [H+] and [OH–] will be displayed in the “result” section along with a Step by Step solution.
How to calculate H+ and OH– using pH and pOH?
The pH and pOH of a solution are related by the equation:
∴ pH + pOH = 14
pH is the negative logarithm of the concentration of H+ ions (represented as [H+]) to the base 10 as shown in the formula given below:
∴ pH = -log10(H+)

The pOH is similarly related to [OH–] and can be calculated as:
∴ pOH = -log10(OH–)

So, we can solve for either [H+] or [OH–] if we know either the pH or pOH value:
∴ [H+] = 10-pH
∴ [OH–] = 10-pOH
Example of calculating H+ and OH– using the “pH and pOH value”
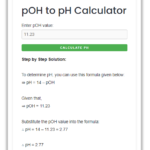
Let’s say we have been given the value of pOH and we need to calculate the [H+] and [OH–] values.
For example – If the pOH value = 9, what are the [H+] and [OH–] values?
As we know the pH and pOH of a solution are related by the equation:
∴ pH + pOH = 14
As pOH is given as 9, therefore, we can calculate the pH value using the above formula:
∴ pH = 14 – pOH = 14 – 9 = 5
The formulas to calculate the H+ and OH– concentrations are:
∴ [H+] = 10-pH
∴ [OH–] = 10-pOH
Substitute the pH and pOH values:
[H+] = 10–5 = 1.00 × 10-5 M
[OH–] = 10–9 = 1.00 × 10-9 M
For example – If the pH value = 11, what are the [H+] and [OH–] values?
As we know the pH and pOH of a solution are related by the equation:
∴ pH + pOH = 14
As pH is given as 11, therefore, we can calculate the pOH value using the above formula:
∴ pOH = 14 – pH = 14 – 11 = 3
The formulas to calculate the H+ and OH– concentrations are:
∴ [H+] = 10-pH
∴ [OH–] = 10-pOH
Substitute the pH and pOH values:
[H+] = 10–11 = 1.00 × 10-11 M
[OH–] = 10–3 = 1.00 × 10-3 M

pH, pOH, H+, and OH– calculation
| pOH | pH | [H+] (M) | [OH–] (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 0 | 1.0 | 1.0 x 10-14 |
| 13 | 1 | 1.0 x 10-1 | 1.0 x 10-13 |
| 12 | 2 | 1.0 x 10-2 | 1.0 x 10-12 |
| 11 | 3 | 1.0 x 10-3 | 1.0 x 10-11 |
| 10 | 4 | 1.0 x 10-4 | 1.0 x 10-10 |
| 9 | 5 | 1.0 x 10-5 | 1.0 x 10-9 |
| 8 | 6 | 1.0 x 10-6 | 1.0 x 10-8 |
| 7 | 7 | 1.0 x 10-7 | 1.0 x 10-7 |
| 6 | 8 | 1.0 x 10-8 | 1.0 x 10-6 |
| 5 | 9 | 1.0 x 10-9 | 1.0 x 10-5 |
| 4 | 10 | 1.0 x 10-10 | 1.0 x 10-4 |
| 3 | 11 | 1.0 x 10-11 | 1.0 x 10-3 |
| 2 | 12 | 1.0 x 10-12 | 1.0 x 10-2 |
| 1 | 13 | 1.0 x 10-13 | 1.0 x 10-1 |
| 0 | 14 | 1.0 x 10-14 | 1.0 |
Numericals based on “OH– and H+ Calculator”
Let’s say we are given a solution with a pH value of 5 and we want to find the concentrations of H+ and OH– ions in this solution. |
We are given a pH of 5 and need to calculate [H+] and [OH–]. We know that [H+] can be calculated from the pH as: ∴ [H+] = 10-pH So, ∴ [H+] = 10-5 = 0.00001 M or 1.0 x 10-5 M Now, Calculate the concentration of OH– ions First, we need to find the pOH, which is related to pH by: ⇒ pOH = 14 – pH ∴ pOH = 14 – 5 = 9 Then, we calculate [OH–] using the pOH as: ∴ [OH–] = 10-pOH ∴ [OH–] = 10-9 = 1.0 x 10-9 M ∴ For a solution with a pH of 5, the concentration of H+ ions is 1.0 x 10-5 M, and the concentration of OH– ions is 1.0 x 10-9 M. |
Suppose we are given a solution with a pOH of 3. We want to determine the concentrations of H+ and OH– ions in this solution. |
We are given a pOH of 3 and need to calculate [H+] and [OH–]. We know that [OH–] can be calculated from the pOH as: ∴ [OH–] = 10-pOH So, ∴ [OH–] = 10-3 = 0.001 M or 1.0 x 10-3 M Now, Calculate the concentration of H+ ions First, we find the pH, which is related to pOH by: ∴ pH = 14 – pOH ∴ pH = 14 – 3 = 11 Then, we calculate [H+] using the pH as: ∴ [H+] = 10-pH ∴ [H+] = 10-11 = 1.0 x 10-11 M ∴ For a solution with a pOH of 3, the concentration of H+ ions is 1.0 x 10-11 M, and the concentration of OH– ions is 1.0 x 10-3 M. |
Also, check
About the author
Vishal Goyal is the founder of Topblogtenz, a comprehensive resource for students seeking guidance and support in their chemistry studies. He holds a degree in B.Tech (Chemical Engineering) and has four years of experience as a chemistry tutor. The team at Topblogtenz includes experts like experienced researchers, professors, and educators, with the goal of making complex subjects like chemistry accessible and understandable for all. A passion for sharing knowledge and a love for chemistry and science drives the team behind the website. Let's connect through LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vishal-goyal-2926a122b/
Related Posts: