Chemistry Regents Reference Table
The Chemistry regents reference table(CRT) is a type of booklet that contains important information such as measurement, equations, charts, formulas, standard values, guidelines for various properties, identification tables, etc related to the chemistry core concept.
The key tables and charts included in the Chemistry reference table:-
| Serial number | Title |
| Table A | Standard temperature and pressure |
| Table B | Physical Constants for Water |
| Table C | Selected Prefixes |
| Table D | Selected Units |
| Table E | Selected Polyatomic Ions |
| Table F | Solubility Guidelines for Aqueous Solutions |
| Table G | Solubility Curves |
| Table H | Vapor Pressure of Four Liquids |
| Table I | Heats of Reaction at 101.3 kPa and 298 K |
| Table J | Activity Series |
| Table K | Common Acids |
| Table L | Common Bases |
| Table M | Common Acid-Base Indicators |
| Table N | Selected Radioisotopes |
| Table O | Symbols Used in Nuclear Chemistry |
| Table P | Organic Prefixes |
| Table Q | Homologous Series of Hydrocarbons |
| Table R | Organic Functional Groups |
| Table S | Properties of selected elements |
| Table T | Important formulas and equations |
Chemistry Reference Table
⇒ Table A: Standard temperature and pressure
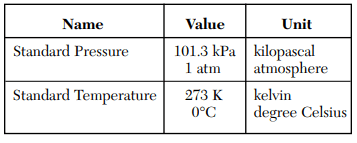
USES:
- This table is commonly used when performing calculations on gases, such as gas density.
- Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) refers to normal conditions in the atmosphere and is used in the matter, energy, and gas law.
- This table is used to convert kPa to atm and K to ºC, and vice-versa.
⇒ Table B: Physical Constants for Water
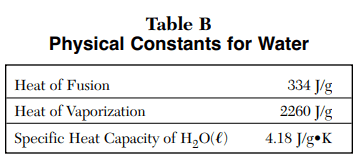
USES:
- This table is also commonly used in Matter, Energy, and Gas law.
- This table is used in the heat energy equation involving water such as Q=mCΔT where C is the specific heat capacity of H2O = 4.18 j/g.K
- Q = mHv where Hv is the heat of vaporization = 2260 j/g.
- Q = mHf where Hf is the heat of fusion = 334 j/g.
⇒ Table C: Selected Prefixes
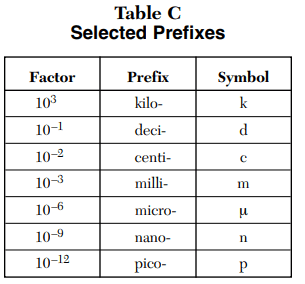
USES:
- This table is used to convert from one unit to another to simplify the problem.
- How many meters are in 100 micrometers? .0001 m
⇒ Table D: Selected Units
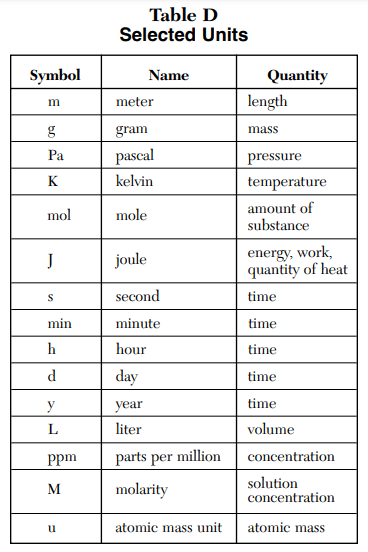
USES:
- This table is used to find the units of a given quantity such as the unit for pressure is pascal and it represented as Pa.
⇒ Table E: Selected Polyatomic Ions
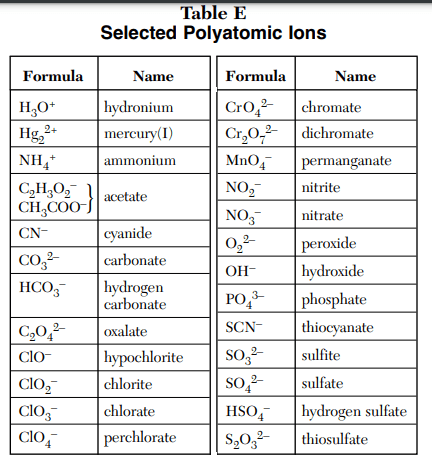
USES:
- This table is used in the Naming, Redox reactions, Balancing, and Formulas writing.
- It is also used to find the charge on the compound. What is the charge of carbonate? -2.
- You can name the compound that includes polyatomic ions. Example – Na2CO3 = Sodium carbonate.
⇒ Table F: Solubility Guidelines for Aqueous Solutions
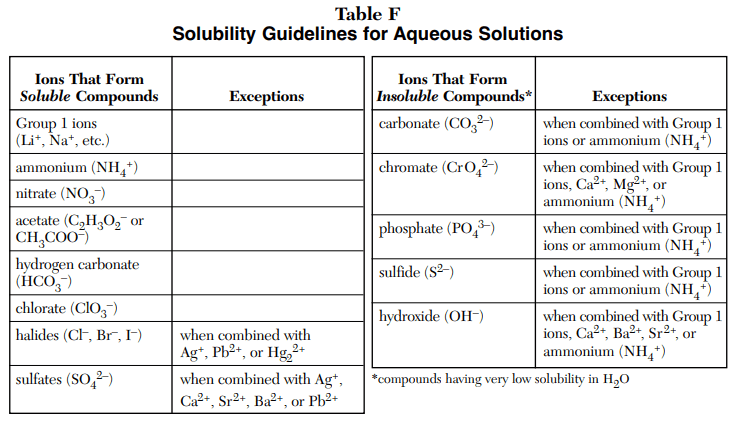
USES:
- This table is used to find if the compound is soluble or not in an aqueous solution.
- The left side table represents soluble and the right side table represent insoluble compound.
⇒ Table G: Solubility Curves
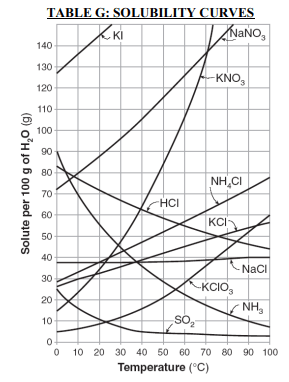
USES:
- “Table G is a graph that shows the solubility of numerous solutes and their ability to dissolve in 100g of H2O.”
- The curves given in the graph represent the greatest amount of solute that “can dissolve at given temperatures.”
⇒ Table H: Vapor Pressure of Four Liquids
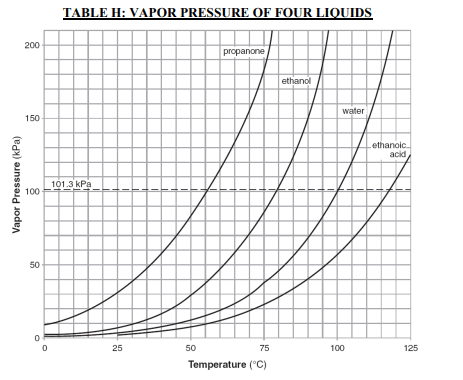
USES:
- This graph is commonly used in the Gas laws problems.
- This graph defines the relationship between the vapor pressure of four liquids and temperature.
- .What is the vapor pressure in kPa and atm of water at 100ºC? 1 atm, 101.3 kPa
⇒ Table I: Heats of Reaction at 101.3 kPa and 298 K
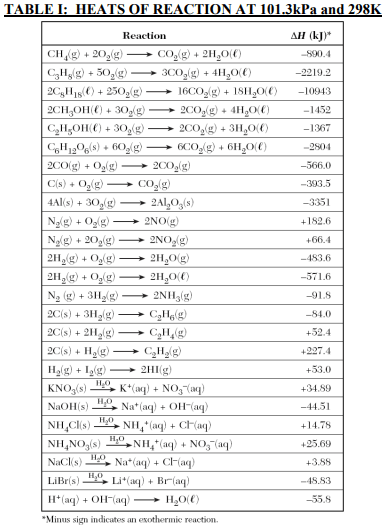
USES:
- This table is used in the kinetics and equilibrium problems.
- This table is used to determine whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic.
- If ΔH is positive then the reaction is endothermic and if the ΔH is negative then the reaction is exothermic.
⇒ Table J: Activity Series
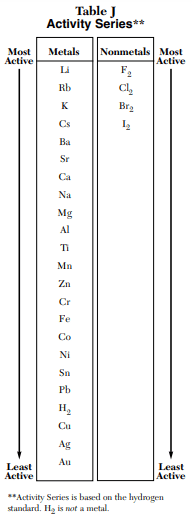
USES:
- This table is used in the Redox and Types of reactions problems.
- This table show metal and nonmetal that at the top of the chart are most active and those at the bottom of the chart are the least active.
- “Table J is also used for electrochemical cell interpretation.”
- Metals at the top are most easily oxidized and Nonmetals at top are most easily reduced.
- Metals at the bottom are least easily oxidized and Nonmetals at the bottom are least easily reduced.
⇒ Table K: Common Acids
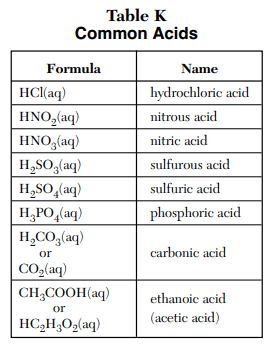
USES:
- This table simply represents some of the most common acids in chemistry.
- Acid is the substance that liberates H+ ions when dissolved in an aqueous solution.
⇒ Table L: Common Bases
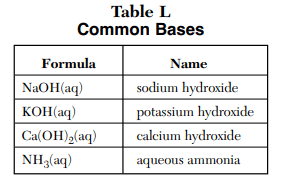
USES:
- This table simply represents some of the most common bases in chemistry.
- The base is the substance that liberates OH– ions when dissolved in an aqueous solution. The exception is NH3 – Also Read – How ammonia (NH3) is base.
⇒ Table M: Common Acid-Base Indicators
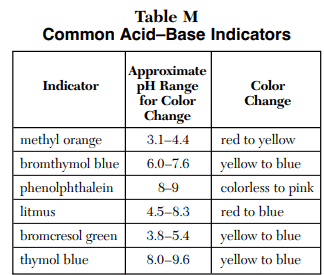
USES:
- This table is used to predict the color change of an indicator in the presence of acid or base at the approximate pH range.
⇒ Table N: Selected Radioisotopes
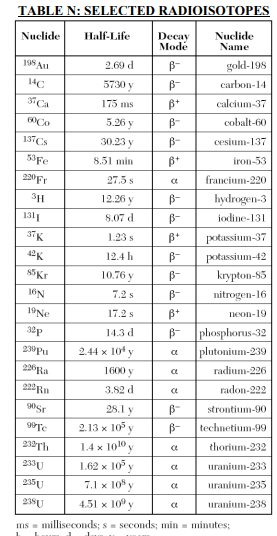
USES:
- “Table N gives a list of radioisotopes, their half-lives, and their decay modes.”
- This table is useful in Nuclear chemistry to solve the problems related to Half-life.
⇒ Table O: Symbols Used in Nuclear Chemistry
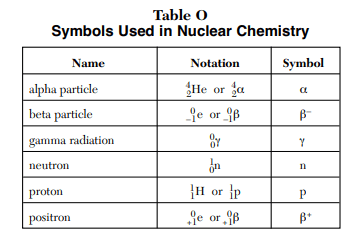
USES:
- “Table O lists common particles associated with nuclear chemistry and nuclear reactions”.
- This table is also used in Nuclear chemistry for writing or figuring out the decay equation.
⇒ Table P: Organic Prefixes
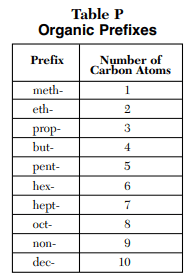
USES:
- Table P is used in organic chemistry to predict the number of carbon atoms in the compound by observing their prefix.
- Example – If the compound is Heptane then according to Table P, it has 7 carbon atoms.
⇒ Table Q: Homologous Series of Hydrocarbons
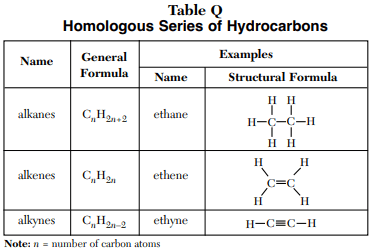
USES:
- This table enlists the three types of hydrocarbons with their structural and general formula.
- This table can be used to recognize and draw the organic compounds.
⇒ Table R: Organic Functional Groups
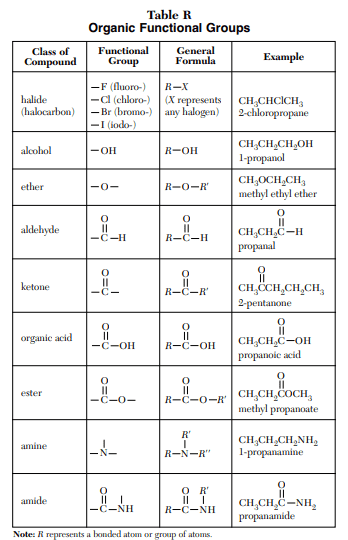
USES:
- This table is used to identify, draw or name the specific organic compounds using functional group and general formulas.
- “Functional groups are specific groupings of atoms within molecules that have their own characteristic properties”.
⇒ Table S: Properties of selected elements
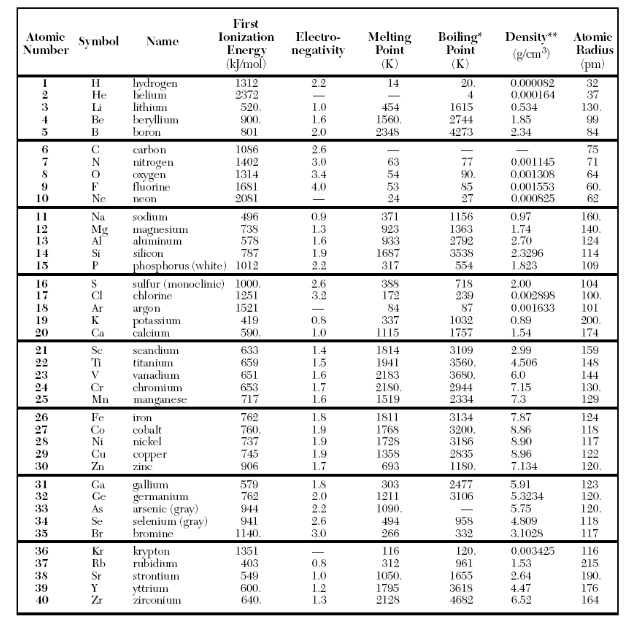
USES:
- This table is used to understand the trends of the periodic table like what happens to electronegativity, atomic radius, ionization energy, atomic number, etc. as you go across a period or as you go down the group.
⇒ Table T: Important formulas and equations
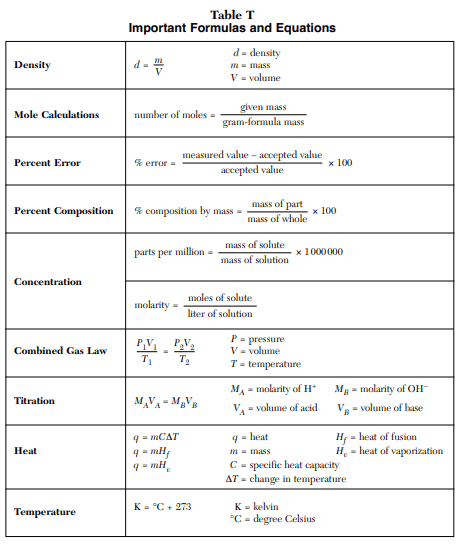
USES:
- This table includes the important formulas and equations that will help you to solve the problems such as calculating percent errors, mole calculations, in Gas law problems, to find specific heat capacity, the heat of fusion, change in temperature, parts per million, etc.
Click here to download the pdf of the Chemistry reference table
The Chemistry Reference Table booklet is used in chemistry regents exams as well as during class, tests, and lab assignments.
Also, read –
- STUDENT TIPS FOR USING THE CHEMISTRY REFERENCE TABLE
- QUESTIONS BASED ON THE CHEMISTRY REFERENCE TABLE
If you are a student or educator who has extensive skills in chemistry, can look toward “chemistry jobs” to earn part-time or even full-time.
Reference:
THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK • THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT• ALBANY, NY 12234: Reference Tables for Physical Setting/CHEMISTRY
“All images are used for only educational purposes, if you are the legal owner of any image we used in this article, please immediately contact us, concerning image will be taken down or will be given proper credit to the original source.”
About the author
Vishal Goyal is the founder of Topblogtenz, a comprehensive resource for students seeking guidance and support in their chemistry studies. He holds a degree in B.Tech (Chemical Engineering) and has four years of experience as a chemistry tutor. The team at Topblogtenz includes experts like experienced researchers, professors, and educators, with the goal of making complex subjects like chemistry accessible and understandable for all. A passion for sharing knowledge and a love for chemistry and science drives the team behind the website. Let's connect through LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vishal-goyal-2926a122b/
