How to draw CO32- lewis structure resonance?
If you find interesting the resonance structures of carbonate (CO32-), a polyatomic molecular ion, then you may like reading this article till the end.
In this article, we will walk you through the possible resonance forms of CO32-, how to draw them, and how the CO32- resonance hybrid is formed from these contributing structures.
So let’s start!
How many resonance structures are possible for CO32-?
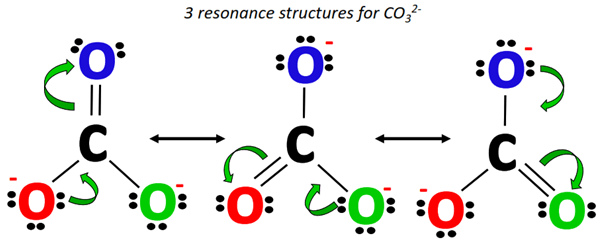
The following three resonance structures represent the carbonate (CO32-) ion.
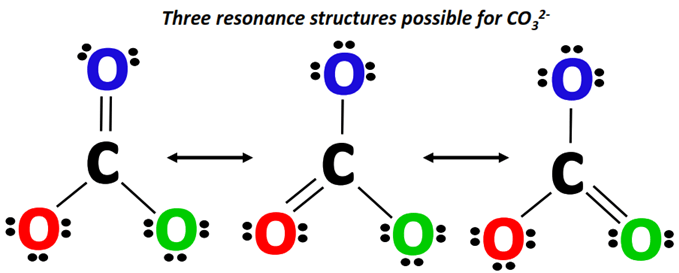
You can draw these resonance structures one by one, following the simple steps given below.
Steps to draw CO32- resonance structures
1. Draw the initial Lewis structure of CO32-
The initial Lewis structure of CO32- is shown below.
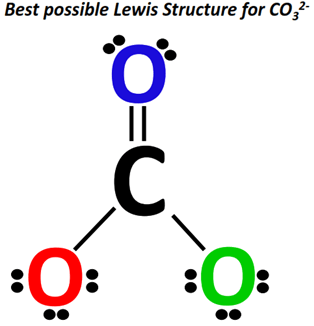
It has a total of 24 valence electrons.
A carbon (C) atom at the center is surrounded by three oxygen (O) atoms at the sides.
Two O-atoms are single-covalently bonded to a C-atom at the center while the third O-atom is single bonded to the central C-atom.
The single-bonded O-atoms have 3 lone pairs each. In contrast, there are 2 lone pairs of electrons on the double-bonded O-atom.
2. Identify the resonance contributing atoms
The terminal oxygen atoms containing lone pairs act as resonance-contributing atoms in CO32-.
3. Determine electron flow and draw the resonance structures
The electron flow is shown using curved arrows.
The C=O double bond keeps shifting its position from one point to another, yielding three different CO32- resonance structures.
Starting from the Lewis structure drawn in step 1, a lone pair from the O-atom (marked red) shifts to form a C=O double bond on the left side of CO32- while the C=O bond at the top of the molecular ion breaks, placing an extra lone pair on the O-atom (marked blue).
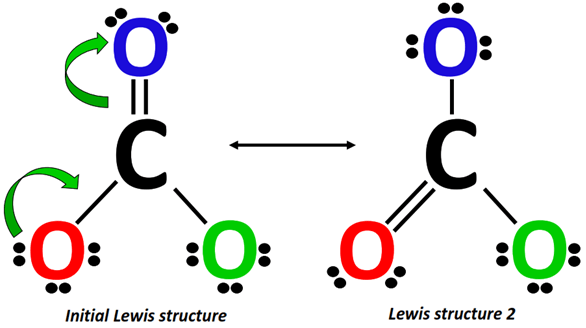
Alternately, from Lewis structure 2, a lone pair from the O-atom (marked green) shifts to form a C=O double bond on the right side of CO32-.
This increase in electron density is accompanied by a simultaneous decrease in electron density as the already present C=O double bond breaks into a single bond, placing an extra lone pair on the O-atom (marked red).
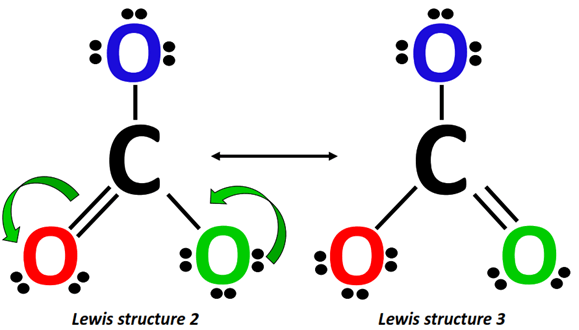
The above two structures along with the Lewis structure drawn in Step 1 make a total of three resonance structures for CO32-.
4. Assign formal charges
The formal charges are assigned using the formula given below:
⇒ Formal charge = (Valence electrons – non-bonding electrons -1/2 bonding electrons)
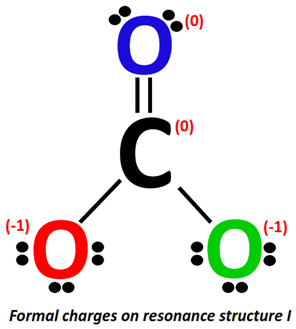
Applying the formal charge formula on resonance structure I:
For C-atom:
- Valence electrons of carbon = 4
- Bonding electrons = 1 double bond + 2 single bonds = 4 + 2(2) = 8 electrons
- Non-bonding electrons = no lone pair = 0 electrons
Formal charge = 4-0-8/2 = 4-0-4 = 4-4 = 0
For O-atom (marked red):
- Valence electrons of oxygen = 6
- Bonding electrons = 1 single bond = 2 electrons
- Non-bonding electrons = 3 lone pairs = 3(2) = 6 electrons
Formal charge = 6-6-2/2 = 6-6-1= 6 – 7 = -1
For O-atom (marked blue):
- Valence electrons of oxygen = 6
- Bonding electrons = 1 double bond = 4 electrons
- Non-bonding electrons =2 lone pairs = 2(2) = 4 electrons
Formal charge = 6-4-4/2 = 6-4-2= 6 –6 = 0
For O-atom (marked green):
- Valence electrons of oxygen = 6
- Bonding electrons = 1 single bond = 2 electrons
- Non-bonding electrons = 3 lone pairs = 3(2) = 6 electrons
Formal charge = 6-6-2/2 = 6-6-1= 6 – 7 = -1
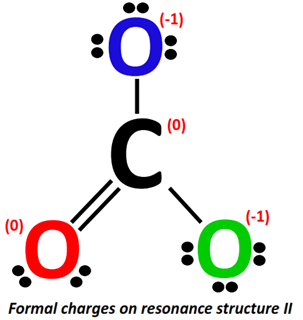
Applying the formal charge formula on resonance structure II:
The formal charge present on the C-atom stays the same i.e., 0.
For O-atom (marked red):
- Valence electrons of oxygen = 6
- Bonding electrons = 1 double bond = 4 electrons
- Non-bonding electrons =2 lone pairs = 2(2) = 4 electrons
Formal charge = 6-4-4/2 = 6-4-2= 6 –6 = 0
For O-atom (marked blue):
- Valence electrons of oxygen = 6
- Bonding electrons = 1 single bond = 2 electrons
- Non-bonding electrons = 3 lone pairs = 3(2) = 6 electrons
Formal charge = 6-6-2/2 = 6-6-1= 6 – 7 = -1
For O-atom (marked green):
- Valence electrons of oxygen = 6
- Bonding electrons = 1 single bond = 2 electrons
- Non-bonding electrons = 3 lone pairs = 3(2) = 6 electrons
Formal charge = 6-6-2/2 = 6-6-1= 6 – 7 = -1
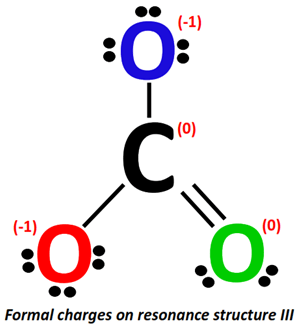
Applying the formal charge formula on resonance structure III:
The formal charge present on the C-atom stays the same i.e., 0.
For O-atom (marked red):
- Valence electrons of oxygen = 6
- Bonding electrons = 1 single bond = 2 electrons
- Non-bonding electrons = 3 lone pairs = 3(2) = 6 electrons
Formal charge = 6-6-2/2 = 6-6-1= 6 –7 = -1
For O-atom (marked blue):
- Valence electrons of oxygen = 6
- Bonding electrons = 1 single bond = 2 electrons
- Non-bonding electrons = 3 lone pairs = 3(2) = 6 electrons
Formal charge = 6-6-2/2 = 6-6-1= 6 –7 = -1
For O-atom (marked green):
- Valence electrons of oxygen = 6
- Bonding electrons = 1 double bond = 4 electrons
- Non-bonding electrons = 2 lone pairs = 2(2) = 4 electrons
Formal charge = 6-4-4/2 = 6-4-2= 6 –6 = 0
5. Combine the resonance structures
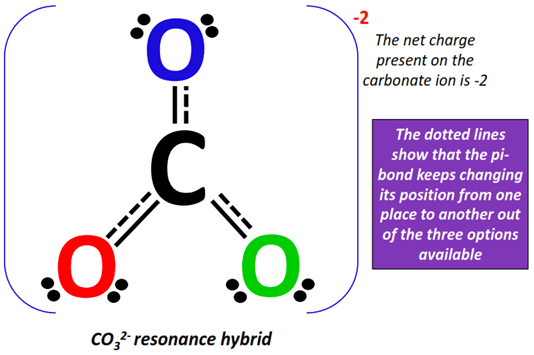
As a final step, the three resonance structures drawn above are combined using double-headed arrows and enclosed in square brackets to represent a single entity i.e., CO32- as shown below.
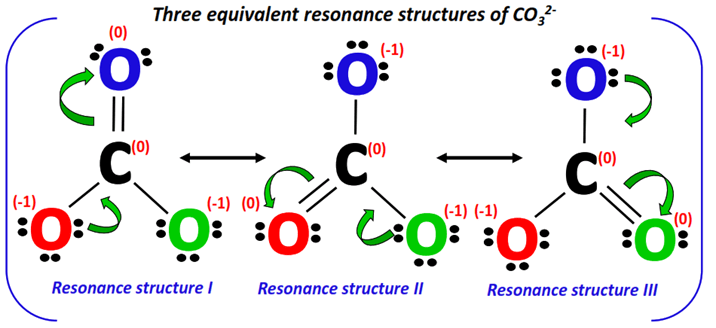
The actual CO32- structure is a weighted average of the above resonance forms. It is known as the resonance hybrid. Each resonance form contributes equally to the resonance hybrid.
The pi-bonds are shown using dotted lines on the resonance hybrid, indicating that it keeps changing its position from one place to another on the ion.
The net charge present on the resonance hybrid = -1 + (-1) = -2.
Therefore, the CO32- resonance hybrid is enclosed in square brackets and a -2 formal charge is placed on the top right corner as shown below.
FAQ
How many resonance structures are there for CO32-? |
Three different resonance structures are possible for CO32- ion are drawn below.
|
Are all three-resonance structures of CO32- equivalent? Why? |
Yes. On account of the same number of formal charges present on the individual atoms, all three resonance structures of CO32- are equivalent, and thus contribute equally to the CO32- resonance hybrid. |
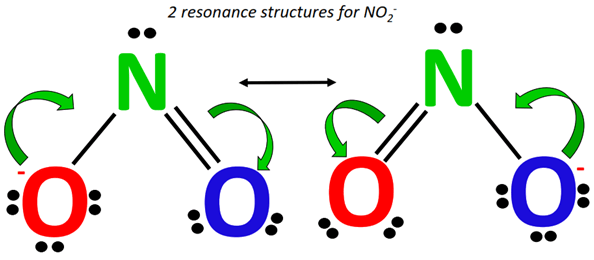
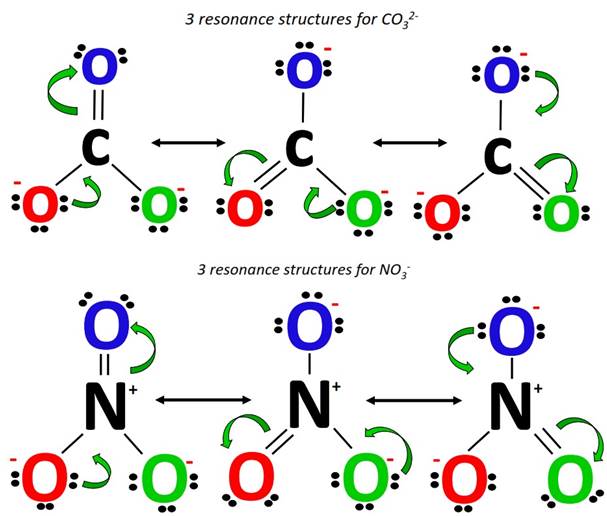
How are the resonance structures of NO2– and NO3– ions similar to or different from that of CO32-? |
NO2– has two equivalent resonance structures, as it possesses 2 resonance-contributing O-atoms.
Contrarily, both NO3– and CO32- possess a total of three equivalent resonance structures as per 3 resonance contributing O-atoms in each of them. These resonance structures look alike. With only the difference in the central atom and the net charge present on the ion, the double bond keeps changing its position, occupying one of the three available options in the NO3– and CO32- resonance structures.
|
What are the formal charges present on CO32- resonance structures? |
The double-bonded O-atom and the central C-atom have zero or no formal charges while each single-bonded O-atom possesses a -1 formal charge in each CO32- resonance structure. |
Do all three CO32- resonance structures have the same number of lone pairs of electrons? |
Yes. All three CO32- resonance structures have 8 lone pairs of electrons each. Maintaining the number of bond pairs and lone pairs constant is the first condition for drawing multiple resonance forms of the same molecule. |
Do CO32- resonance structures follow the octet rule? |
Yes. The central C-atom and each of the three O-atoms follow the octet rule in each resonance structure of CO32-, possessing a total of 8 valence electrons. |
About the author
Vishal Goyal is the founder of Topblogtenz, a comprehensive resource for students seeking guidance and support in their chemistry studies. He holds a degree in B.Tech (Chemical Engineering) and has four years of experience as a chemistry tutor. The team at Topblogtenz includes experts like experienced researchers, professors, and educators, with the goal of making complex subjects like chemistry accessible and understandable for all. A passion for sharing knowledge and a love for chemistry and science drives the team behind the website. Let's connect through LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vishal-goyal-2926a122b/

![How to find pOH from molarity?, [pOH from hydroxide (OH-) ion] formula to find pOH from molarity (hydroxide ion concentration)](https://topblogtenz.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/formula-to-find-pOH-from-molarity-hydroxide-ion-concentration-min-150x150.png)
