Is Hydrogen bromide (HBr) an acid or base? Strong or Weak - Conjugate base

Hydrogen bromide belongs to the hydrogen halide family consist of one bromine and one hydrogen with the chemical formula HBr. It appears as a colorless gas with a pungent odor. Exposure to this gas can cause suffocation.
Hydrogen bromide is highly soluble in water and readily fumes in the presence of moist air. It is corrosive and heavier than air.
In this article, we will discuss Is Hydrogen bromide (HBr) is an acid or base? Its nature(Strong or weak, Conjugates acid-base pairs, etc.
So, Is HBr an acid or base? HBr is considered an acid. Because on dissolving in an aqueous solution it dissociates into two ions (H+ and Br–), and anything that liberates proton ion in a solution, is considered the acid in nature. It has a pH value of 3.01 in 1mM solution.
| Name of Molecule | Hydrobromic acid |
| Chemical formula | HBr |
| Molar mass | 80.91 g·mol−1 |
| Nature | Strong acid |
| Conjugate base | Br– |
| pH value | 3.01 |
Why HBr is an acid?
To Know Why HBr is acting as an acid? We have to look into the famous theory given by Arrhenius for the acid compounds.
This theory state that a compound is said to be acid when it produces H+ ions on dissolving in an aqueous solution and forms H3O+ ions when combined with the water molecule.
Now have a look at HBr dissociation in an aqueous solution.
⇒ HBr → H+ + Br–
As on dissolving HBr in an aqueous solution, it dissociates into two ions H+ and Br–. Then, a proton ion(H+) combines with a water molecule and forms H3O+.
⇒ HBr(g) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + Br−(aq)

Also, Arrhenius sate that an acid is a compound that increases the concentration of hydrogen ion(H+) in solution.
In the case of the HBr compound, when dissolved in an aqueous solution it liberates one H+ ion, hence increasing the concentration of hydrogen ion in the final solution.
So, the HBr compound definitely follows all conditions needs to meet for the Arrhenius acid compound. Hence, we can say the HBr is an Arrhenius acid compound.
Now we look for another most important acid-base theory that is the Bronsted-Lowry theory.
This theory states a compound is classified as an acid when it donates the proton to other species and itself forms a conjugate base. And a compound is classified as a base when it accepts the proton from other species and itself forms a conjugate acid.
In short as per Bronsted-Lowry theory–
- A Bronsted-Lowry acid is a proton (hydrogen ion) donor.
- A Bronsted-Lowry base is a proton (hydrogen ion) acceptor.
Let’s check whether HBr fulfills the requirement for classifying as Bronsted-Lowry acid or not.
Consider the reaction of HBr reacting with NH3.
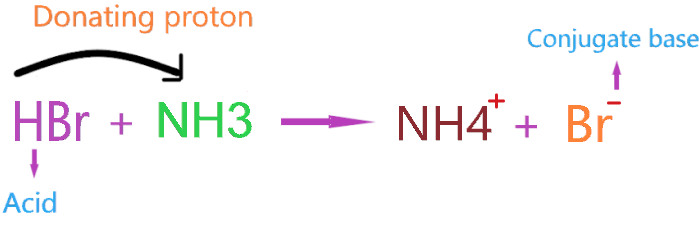
Here, HBr reacts with ammonia and donates the proton which is accepted by NH3 and itself forms Br– conjugate base.
Illustration of above reaction (HBr with NH3):-
- HBr act as Bronsted-Lowry acid as it donates the proton and forms a conjugate base.
- NH3 acts as a Bronsted-Lowry base as it accepts the proton from HBr and forms a Conjugate acid.
- Ammonium ion (NH4+) is the conjugate acid of the base NH3.
- Bromine ion(Br–) is the conjugate base of the acid HBr.
Is Hydrobromic (HBr) acid strong or weak?
A strong acid is something that completely dissociates or is 100% ionized in a solution. Some examples of strong acids – are HCl, HI, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO4, etc.
Also, Read:-
- Is H2SO4 a strong acid?
- Is HNO3 a strong acid?
- Is HCl a strong acid?
- Is HI a strong acid?
- Is HClO4 a strong acid?
Characteristics of strong acid:-
- They are strong electrolytes and have high conductivity.
- Their pH value lies between 1 to 3.
- They dissociate completely and release a large number of H+ ions in a solution.
A weak acid is something that is not able to dissociate completely or partially dissociate in solution. Some examples of weak acids – are CH3COOH, HF, HCN, HNO2, HCOOH, H2CO3, H3PO4, NH4+, etc.
Also, Read:-
- Is CH3COOH a weak acid?
- Is HF a weak acid?
- Is HCN a weak acid?
- Is HNO2 a weak acid?
- Is HCOOH a weak acid?
- Is H3PO4 a weak acid?
- Is H2CO3 a weak acid?
- Is NH4+ a weak acid?
Characteristics of Weak acids:-
- They are weak electrolytes and have less conductivity as compared to strong acids.
- Their pH value lies between 3 to 7.
- They ionized partially to produce H+ in a solution.
Now, Is HBr a strong or weak acid? HBr is a strong acid because it readily dissociates in an aqueous solution, which means no undissociated parts of it remain in the solution, all parts completely break off and are ionized in an aqueous solution.
Why HBr easily breaks off and dissociate readily in an aqueous solution?
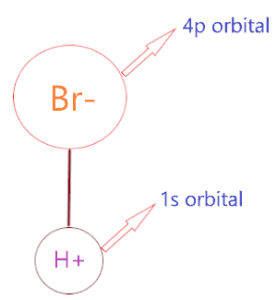
HBr can easily break off because the bond strength of the H-Br bond is very weak due to the large gap in the orbital size of these ions. As the orbital size for H is 1s and for Br atom, it is 4p.
Hence, overlapping of 1s and 4p orbital becomes very small, this cause binding between H-Br very weak in nature, hence the covalent bond in H-Br atom easily break off and makes it readily dissociate in aqueous to liberate H+ ion.
More reasons, why HBr act as strong acid?
As we know, halogen atoms have very high electronegativity and a high energy level, these make a halogen atom size bigger and hydrogen is just opposite to it. So, the attraction between bromine and hydrogen becomes very weak.
Therefore, Hydrogen easily breaks off from HBr due to its small size and causes HBr to readily dissociates in an aqueous solution and completely splits into two ions (H+ and Br–).
Also Read:
What is the conjugate base of HBr?
Whenever the acid donates the proton, it converts into the conjugate base and whenever the base accepts the proton, it converts into the conjugate acid.
Conjugate acid is an acid that is formed when the base compound gains one proton and the conjugate base is a base that is formed when the acid compound loses one proton.
The concept of conjugate acid-base pair.
- A very strong acid always forms a weak conjugate base.
- A very strong base always forms a weak conjugate acid.
- A very weak acid always forms a strong conjugate base.
- A very weak base always forms a strong conjugate acid.
As per Bronsted-Lowry, HBr is acid and loses one proton when combined with the water molecule and forms a base known as the conjugate base of an acid(HBr).
∴ The conjugate base of HBr is Br–.
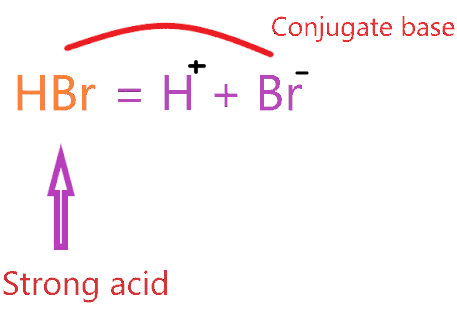
Is HBr Lewis acid or base?
When the compound accepts the pair of electrons from another compound classified as Lewis acid and when the compound donates the pair of electrons to another compound classified as Lewis base.
⇒ Lewis acid → electron pair acceptor
⇒ Lewis base → electron pair donator
Now, Is HBr lewis acid or base? Definitely, HBr is a lewis acid because it accepts one lone pair when combining with a water molecule, forms hydronium ion and Br– conjugate base.
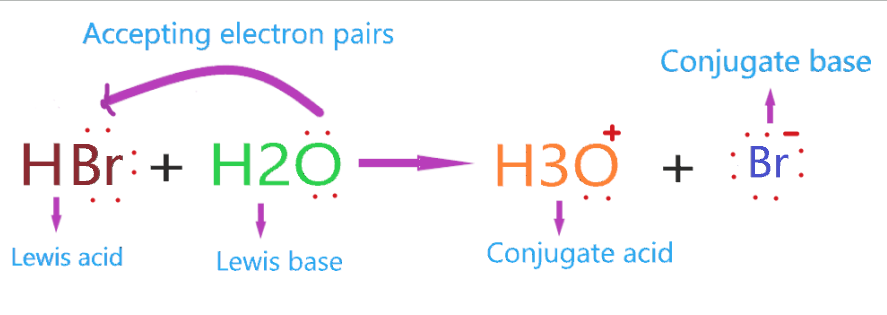
As bromine is more electronegative than hydrogen and has 3 lone around it, being more electronegative it attracts more electron towards itself, hence a negative charge induces on the bromine atom and a positive charge on the hydrogen atom.
The lone pair on the water molecule(H2O) attracted slightly to the hydrogen atom, also more electrons repelled towards the Bromine atom due to its negative charge.
Furthermore, a coordinate bond formed between oxygen and hydrogen, and the bromine breaks away as a Bromide ion.
So, the whole HBr molecule acts as lewis acid as it accepts the lone pair of electrons from H2O, and in this process, the Bromide ion breaks off.
Uses of Hydrobromic acid
- Hydrobromic acid is used to produce bromides of sodium, zinc, and calcium.
- Hydrobromic used as participates in antiMarkovnikov hydrohalogenation of alkenes.
- In organic reactions, HBr used as a reagent and as a catalyst.
- It is also used as a sanitizing or disinfecting agent.
Properties of Hydrobromic acid
- HBr gas is highly corrosive and causes severe burn upon contact.
- It has a pKa value of -9.
- It is one of the strongest mineral acids and stronger acids than HCl.
- It has a boiling point of 122 °C and a melting point of −11 °C.
- It readily fumes in the presence of moist air.
- It is non-flammable.
Summary
Hydrogen bromide is an inorganic compound that appears as a colorless gas with a pungent odor having a pH value of 3.01. When hydrogen bromide dissolved in water, it forms hydrobromic acid. At last, with some important points of this article on Is HBr an acid or base? we will finish it.
- HBr is an acid. It liberates the H+ ions when dissolved in an aqueous solution, therefore, increasing the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution, which shows its acidic nature.
- HBr is lewis acid. Because of lone pair electrons accepting ability from another compound.
- The conjugate base of HBr is Br–, as it formed after the removal of one proton from HBr.
- Is Hydrobromic (HBr) is a strong or weak acid? HBr is not only strong acid but it is one of the strongest minerals acids as it completely breaks off when dissolved in an aqueous solution, which means it doesn’t leave any traces of its parts in an aqueous solution, all parts of it completely ionized in solution and increases the concentration of hydrogen ions.
About the author
Vishal Goyal is the founder of Topblogtenz, a comprehensive resource for students seeking guidance and support in their chemistry studies. He holds a degree in B.Tech (Chemical Engineering) and has four years of experience as a chemistry tutor. The team at Topblogtenz includes experts like experienced researchers, professors, and educators, with the goal of making complex subjects like chemistry accessible and understandable for all. A passion for sharing knowledge and a love for chemistry and science drives the team behind the website. Let's connect through LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vishal-goyal-2926a122b/